Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Posterior pituitary
| Posterior pituitary | |
|---|---|
 Pituitary gland. Posterior pituitary is in blue and Anterior pituitary is in orange. Pars nervosa and infundibular stalk are not labeled, but pars nervosa is at bottom and infundibular stalk is at top. | |
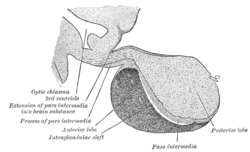 Median sagittal through the hypophysis of an adult monkey. (Posterior lobe labeled at bottom right.) | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Neural tube (downward-growth of the diencephalon)[1] |
| Artery | Inferior hypophyseal artery |
| Vein | Hypophyseal vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | pars nervosa glandulae pituitariae, pars nervosa hypophyseos, lobus posterior hypophyseos |
| MeSH | D010904 |
| NeuroNames | 401 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1586 |
| TA98 | A11.1.00.006 |
| TA2 | 3859 |
| FMA | 74636 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland which is part of the endocrine system. The posterior pituitary is not glandular as is the anterior pituitary. Instead, it is largely a collection of axonal projections from the hypothalamus that terminate behind the anterior pituitary, and serve as a site for the secretion of neurohypophysial hormones (oxytocin and vasopressin) directly into the blood.[2] The hypothalamic–neurohypophyseal system is composed of the hypothalamus (the paraventricular nucleus and supraoptic nucleus), posterior pituitary, and these axonal projections.[2]
- ^ Embryology at unc.edu
- ^ a b Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 10: Neural and Neuroendocrine Control of the Internal Milieu". In Sydor A, Brown RY (ed.). Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 246, 248–259. ISBN 9780071481274.
•The hypothalamic–neurohypophyseal system secretes two peptide hormones directly into the blood, vasopressin and oxytocin. ...
•The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis. It comprises corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF), released by the hypothalamus; adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), released by the anterior pituitary; and glucocorticoids, released by the adrenal cortex.
•The hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis consists of hypothalamic thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH); the anterior pituitary hormone thyroid–stimulating hormone (TSH); and the thyroid hormones T3 and T4.
•The hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis comprises hypothalamic gonadotropin–releasing hormone (GnRH), the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and the gonadal steroids.
Previous Page Next Page


