Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
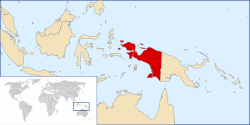
Republic of West Papua
Republic of West Papua Republik Papua Barat | |
|---|---|
| Motto: One People One Soul | |
| Anthem: Hai Tanahku Papua (Indonesian) (English: "Oh My Land Papua") | |
 | |
| Status | Quasi-state |
| Capital | Jayapura (claimed) |
| Common languages | Indonesian, Papuan Malay, and Papuan languages Dutch and English (in exile) |
| Religion | Christianity, Animism, Islam |
| Demonym(s) | Papuan |
| Government | Provisional government[1][2][a] |
| Establishment | |
| 27 December 1949 | |
• Inauguration ceremony and proclamation | 1 December 1961 |
| 1 October 1962 | |
| 1 May 1963 | |
| 19 November 1969 | |
• Free Papua Movement proclaimed republic | 1 July 1971 |
• Dr. Thomas Wainggai proclaimed republic | 14 December 1988 |
• West Papua National Authority proclaimed federal republic[4] | 19 October 2011 |
The Republic of West Papua (Indonesian: Republik Papua Barat), alternatively known as the Federal Republic of West Papua (Indonesian: Republik Federal Papua Barat, RFPB) is a quasi-state consisting of the Western New Guinea region, which is currently part of Indonesia on the continent of Oceania. The region has been part of Indonesia since 1 May 1963 under several names in the following order, West Irian, Irian Jaya, and Papua. Today the region comprises six Indonesian provinces: Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, South Papua, West Papua, and Southwest Papua.
The proposal is supported by the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu with the Parliament of Vanuatu passing the Wantok Blong Yumi Bill (Our Close Friends) in 2010, officially declaring that Vanuatu's foreign policy is to support the achievement of the independence of West Papua.[5][6][7] The parliament has proposed requesting that West Papua be granted observer status at the Melanesian Spearhead Group and Pacific Islands Forum.[8][9][10]
The Republic of West Papua has been a member state of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization (UNPO) since the organization's founding in 1991.[11]
- ^ "West Papua independence leaders declare 'government-in-waiting'". The Guardian. 30 November 2020. Retrieved 28 May 2021.
- ^ Namita Singh (1 Dec 2020). ""Benny Wenda proclaimed provisional (in waiting) government"". Independent.co.uk. Retrieved 28 May 2021.
- ^ "Vanuatu's Shefa province recognises West Papua government". Radio New Zealand. 3 December 2021.
- ^ "Provisional government of west papua". federalstatesofwestpapua. Retrieved 28 May 2021.
- ^ "Fiery debate over West Papua at UN General Assembly". Radio New Zealand 2017. 27 September 2017. Retrieved 7 October 2017.
- ^ "Indonesia hits back at Melanesian leaders on West Papua". Radio New Zealand. 27 September 2017. Retrieved 7 October 2017.
- ^ Manning, Selwyn (22 June 2010). "Vanuatu to seek observer status for West Papua at MSG and PIF leaders summits". Pacific Scoop. Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- ^ Buchanan, Kelly (2010-07-21). "Indonesia; Vanuatu: Vanuatu Parliament Passes Resolution on West Papua Independence". www.loc.gov. Retrieved 2018-05-02.
- ^ "Vanuatu to seek UN General Assembly support for ICJ opinion on Indonesia's Papua". Radio New Zealand. 2010-06-21. Retrieved 2018-05-02.
- ^ "Pacific.scoop.co.nz » Vanuatu to seek observer status for West Papua at MSG and PIF leaders summits". pacific.scoop.co.nz. Retrieved 2018-05-02.
- ^ Simmons, ed. (14 August 1996). Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Yearbook 1995. Kluwer Law International. pp. 1–3. ISBN 90-411-0223-X.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
Previous Page Next Page
جمهورية بابوا الغربية Arabic باتی پاپوآ جومهوریتی AZB Көнбайыш Папуа Республикаһы BA Republik Westpapua German Δημοκρατία της Δυτικής Παπούα Greek República de Papúa Occidental Spanish Mendebaldeko Papuako Errepublika EU جمهوری پاپوآی غربی FA Länsi-Papuan tasavalta Finnish République de Papouasie occidentale French




