Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Rifaximin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xifaxan, others[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a604027 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | < 0.4% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 6 hours |
| Excretion | Fecal (97%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.111.624 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
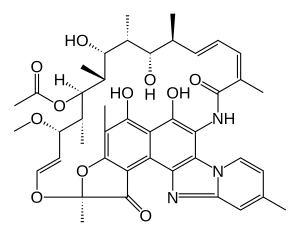
| Formula | C43H51N3O11 |
| Molar mass | 785.891 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 200 to 205 °C (392 to 401 °F) (dec.) |
| |
| |
| | |
Rifaximin, sold under the brand name Xifaxan among others, is a non-absorbable, broad-spectrum antibiotic mainly used to treat travelers' diarrhea. It is based on the rifamycin antibiotics family. Since its approval in Italy in 1987, it has been licensed in more than 30 countries for the treatment of a variety of gastrointestinal diseases like irritable bowel syndrome and hepatic encephalopathy. It acts by inhibiting RNA synthesis in susceptible bacteria by binding to the RNA polymerase enzyme. This binding blocks translocation, which stops transcription.[4] It was developed by Salix Pharmaceuticals.[3][5][6]
- ^ "Rifaximin international". Drugs.com. 2 November 2020. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ "Product monograph brand safety updates". Health Canada. February 2024. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ a b "Xifaxan- rifaximin tablet". DailyMed. 1 October 2019. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ Koo HL, DuPont HL (January 2010). "Rifaximin: a unique gastrointestinal-selective antibiotic for enteric diseases". Current Opinion in Gastroenterology. 26 (1): 17–25. doi:10.1097/MOG.0b013e328333dc8d. PMC 4737517. PMID 19881343.
- ^ "Drug Approval Package: Xifaxan (Nfaximin) NDA #021361". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 28 December 2024.
- ^ "Drug Approval Package: Xifaxan (rifaximin) NDA #022554". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 26 July 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2024.
Previous Page Next Page


