Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Rotifer
| Rotifera Temporal range: Possible Devonian and Permian records
| |
|---|---|
| |
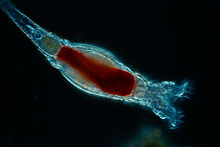
| Bdelloid rotifer (Bdelloidea) | |
| |
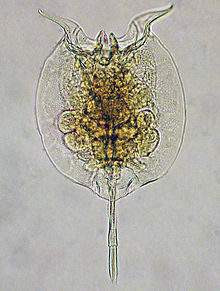
| Pulchritia dorsicornuta (Monogononta) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Clade: | Bilateria |
| Clade: | Nephrozoa |
| Clade: | Protostomia |
| (unranked): | Spiralia |
| Clade: | Gnathifera |
| Phylum: | Rotifera Cuvier, 1798 |
| Classes and other subgroups | |
The rotifers (/ˈroʊtɪfərz/, from Latin rota 'wheel' and -fer 'bearing'), sometimes called wheel animals or wheel animalcules,[1] make up a phylum (Rotifera /roʊˈtɪfərə/) of microscopic and near-microscopic pseudocoelomate animals.
They were first described by Rev. John Harris in 1696, and other forms were described by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1703.[2] Most rotifers are around 0.1–0.5 mm (0.0039–0.0197 in) long (although their size can range from 50 μm (0.0020 in) to over 2 mm (0.079 in)),[1] and are common in freshwater environments throughout the world with a few saltwater species.
Some rotifers are free swimming and truly planktonic, others move by inchworming along a substrate, and some are sessile, living inside tubes or gelatinous holdfasts that are attached to a substrate. About 25 species are colonial (e.g., Sinantherina semibullata), either sessile or planktonic. Rotifers are an important part of the freshwater zooplankton, being a major foodsource and with many species also contributing to the decomposition of soil organic matter.[3] Most species of the rotifers are cosmopolitan, but there are also some endemic species, like Cephalodella vittata to Lake Baikal.[4] Recent barcoding evidence, however, suggests that some 'cosmopolitan' species, such as Brachionus plicatilis, B. calyciflorus, Lecane bulla, among others, are actually species complexes.[5][6] In some recent treatments, rotifers are placed with acanthocephalans in a larger clade called Syndermata.
In June 2021, biologists reported the restoration of bdelloid rotifers after being frozen for 24,000 years in the Siberian permafrost.[7][8] Early purported fossils of rotifers have been suggested in Devonian[9] and Permian[10] fossil beds.
- ^ a b Howey, Richard L. (1999). "Welcome to the Wonderfully Weird World of Rotifers". Micscape Magazine. Retrieved 19 February 2010.
- ^ Harmer, Sidney Frederic & Shipley, Arthur Everett (1896). The Cambridge Natural History. The Macmillan company. pp. 197. Retrieved 25 July 2008.
john harris rotifer.
- ^ "Rotifers". Freshwater Life. Archived from the original on 1 August 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2010.
- ^ Hendrik Segers (2007). Annotated checklist of the rotifers (Phylum Rotifera), with notes on nomenclature, taxonomy
- ^ Gómez, Africa; Serra, Manuel; Carvalho, Gary R.; Lunt, David H. (July 2002). "Speciation in ancient cryptic species complexes: evidence from the molecular phylogeny of Brachionus plicatilis (Rotifera)". Evolution; International Journal of Organic Evolution. 56 (7): 1431–1444. doi:10.1111/j.0014-3820.2002.tb01455.x. ISSN 0014-3820. PMID 12206243.
- ^ Dec 2011 4th Internat. Barcode of Life conference, University of Adelaide
- ^ Renault, Marion (7 June 2021). "This Tiny Creature Survived 24,000 Years Frozen in Siberian Permafrost - The microscopic animals were frozen when woolly mammoths still roamed the planet, but were restored as though no time had passed". the New York Times. Retrieved 8 June 2021.
- ^ Shmakova, Lyubov; Malavin, Stas; Iakovenko, Nataliia; Vishnivetskaya, Tatiana; Shain, Daniel; Plewka, Michael; Rivkina, Elizaveta (June 2021). "A living bdelloid rotifer from 24,000-year-old Arctic permafrost". Current Biology. 31 (11): R712 – R713. Bibcode:2021CBio...31.R712S. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2021.04.077. PMID 34102116. S2CID 235365588.
- ^ "Spoilt attack in the Lower Devonian".
- ^ "The Oldest Bdelloid Rotifera from Early Permian sediments of Chamba Valley: A New Discovery". International Journal of Geology, Earth and Environmental Science.
Previous Page Next Page


