Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
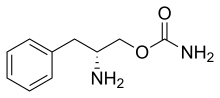
Solriamfetol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Sunosi |
| Other names | SKL-N05, ADX-N05, ARL-N05, YKP10A, R228060, and JZP-110; (R)-2-amino-3-phenylpropylcarbamate hydrochloride |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a619040 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth[1] |
| Drug class | Norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitors; Wakefulness-promoting agents; Psychostimulants |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~95%[1] |
| Protein binding | 13.3–19.4%[1] |
| Metabolism | Minimal (~1%)[1] |
| Metabolites | • N-Acetylsolriamfetol (~1%)[1] |
| Elimination half-life | ~7.1 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Urine (95% unchanged) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H14N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 194.234 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Solriamfetol, sold under the brand name Sunosi, is a wakefulness-promoting medication used in the treatment of excessive sleepiness related to narcolepsy and sleep apnea.[1][5][6] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects of solriamfetol include headache, nausea, anxiety, and trouble sleeping.[1] It is a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) and is thought to work by increasing levels of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and dopamine in the brain.[1][5] Solriamfetol has also been found to act as a TAAR1 agonist, an action that may also be involved in its effects.[7]
The drug was discovered by a subsidiary of SK Group, which licensed rights outside of eleven countries in Asia to Aerial Pharma in 2011.[8] In addition to its approved indication of excessive sleepiness, solriamfetol is under development for certain other uses including the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), binge eating disorder, and circadian rhythm sleep disorders.[9]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Sunosi – solriamfetol tablet, film coated". DailyMed. 16 October 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- ^ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Sunosi". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- ^ "Health product highlights 2021: Annexes of products approved in 2021". Health Canada. 3 August 2022. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Sunosi EPARwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Powell J, Piszczatoski C, Garland S (October 2020). "Solriamfetol for Excessive Sleepiness in Narcolepsy and Obstructive Sleep Apnea". Ann Pharmacother. 54 (10): 1016–1020. doi:10.1177/1060028020915537. PMID 32270686. S2CID 215605290.
- ^ Abad VC, Guilleminault C (December 2018). "Solriamfetol for the treatment of daytime sleepiness in obstructive sleep apnea". Expert Rev Respir Med. 12 (12): 1007–1019. doi:10.1080/17476348.2018.1541742. PMID 30365900. S2CID 53106520.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
GursahaniJolasMartin2023was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Ji-young S (5 March 2018). "SK Biopharmaceuticals' narcolepsy drug on track to hitting US market". The Korea Herald.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
AdisInsightwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
Previous Page Next Page


