Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Spanish Texas
| History of Texas | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
| History of Spain |
|---|
 18th century map of Iberia |
| Timeline |
Spanish Texas was one of the interior provinces of the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1519 until 1821. Spain claimed ownership of the region in 1519. Slave raids by Spaniards into what became Texas began in the 16th century and created an atmosphere of antagonism with Native Americans (Indians) which would cause endless difficulties for the Spanish in the future. Spain did not attempt to establish a permanent presence until after France established the colony of Fort Saint Louis in 1685. In 1688, the French colony failed due to internal dissention and attacks by the Karankawa Indians. In 1690, responding to fear of French encroachment, Spanish explorer Alonso de León escorted several Catholic missionaries to east Texas, where they established the first mission in Texas. That attempt to establish a Spanish colony failed due to the hostility of the Caddo Indians.
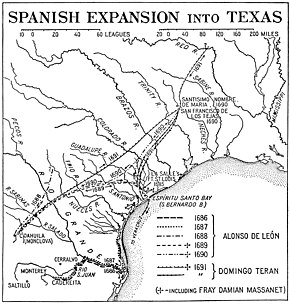
The Spanish returned to southeastern Texas in 1716, establishing several missions and a presidio to maintain a buffer between Spanish territory and the Louisiana district of New France. San Antonio was founded in 1719 and became the capital and largest settlement of Spanish Tejas. The Lipan Apache menaced the newly founded colony until 1749 when the Spanish and Lipan concluded a peace treaty. Both the Spanish and Lipan were then threatened by Comanche raids until 1785 when the Spanish and Comanche negotiated a peace agreement. In 1803, the United States gained ownership of an indefinite part of Texas with the Louisiana Purchase and subsequently the influence of Anglo Americans increased.
During the Mexican War of Independence from 1810 to 1821 Texas experienced turmoil. Reaching a maximum population of perhaps 5,000 Spanish, mixed blood, and subject Indians in 1810, only 2,500 people remained in Hispanic Texas by the end of the war. Mexico gained its independence from Spain in 1821 and Spanish Texas became part of an independent Mexico. Texas became independent of Mexico in 1836 and joined the United States in 1845.
The Spanish never achieved control of most of Texas which was on the far frontier of Spanish colonial ambitions. Despite the meager nature of Spanish colonization, Hispanic influence in Texas is extensive. Spanish architectural concepts still flourish. Many cities and rivers in Texas were named by the Spanish and many counties in southern and western Texas have majority Hispanic populations. The inadvertent introduction of European diseases by the Spanish caused Native American populations to plummet, leaving a population vacuum later filled by Anglo American settlers. Grazing of European livestock caused mesquite to spread inland replacing native grassland while Spanish farmers tilled and irrigated the land and changed the landscape. Although Texas eventually adopted much of the Anglo-American legal system, many Spanish legal practices survived, including the concepts of a homestead exemption and of community property.
Previous Page Next Page


