Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Spermatogonium
| Spermatogonium [1] | |
|---|---|
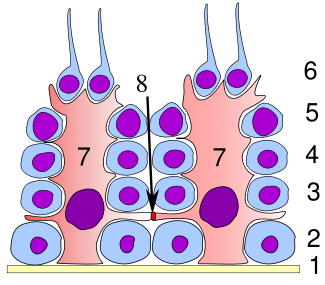 Germinal epithelium of the testicle. 1 basal lamina, 2 spermatogonia, 3 spermatocyte 1st order, 4 spermatocyte 2nd order, 5 spermatid, 6 mature spermatid, 7 Sertoli cell, 8 tight junction (blood testis barrier) | |
 Histological section through testicular parenchyma of a boar. 1 Lumen of Tubulus seminiferus contortus, 2 spermatids, 3 spermatocytes, 4 spermatogonia, 5 Sertoli cell, 6 myofibroblasts, 7 Leydig cells, 8 capillaries | |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D013093 |
| FMA | 72291 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A spermatogonium (plural: spermatogonia) is an undifferentiated male germ cell. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles.
There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in humans:
Type A (dark) cells, with dark nuclei. These cells are reserve spermatogonial stem cells which do not usually undergo active mitosis. Type A (pale) cells, with pale nuclei. These are the spermatogonial stem cells that undergo active mitosis. These cells divide to produce Type B cells. Type B cells, which undergo growth and become primary spermatocytes.
- ^ Mahla, R.S. (2012). "Spermatogonial Stem Cells (SSCs) in Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Testis". PLOS ONE. 7 (4): e36020. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...736020M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036020. PMC 3334991. PMID 22536454.
Previous Page Next Page


