Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Strain wave gearing
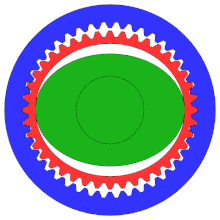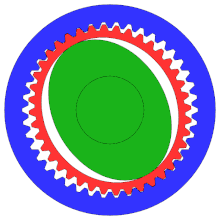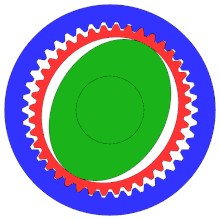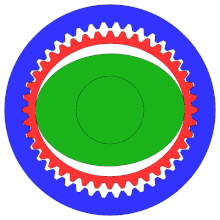
- Outer circle: circular spline (fixed)
- Middle circle: flex spline (attached to output shaft, not shown)
- Inner oval: wave generator (attached to input shaft; inner ball bearing and shaft, not shown)

Strain wave gearing (also known as harmonic gearing) is a type of mechanical gear system that uses a flexible spline with external teeth, which is deformed by a rotating elliptical plug to engage with the internal gear teeth of an outer spline.
The German company Harmonic Drive SE manufactured the first series-produced gears under the product name or registered trademark Harmonic Drive.
Strain wave gearing has some advantages over traditional gearing systems such as helical or planetary gears, including:
- no backlash,
- compactness and light weight,
- high gear ratios,
- reconfigurable ratios within a standard housing,
- good resolution and excellent repeatability (linear representation) when repositioning inertial loads,[1]
- high torque capability,
- coaxial input and output shafts.[2]
High gear reduction ratios are possible in a small volume (a ratio from 30:1 up to 320:1 is possible in the same space in which planetary gears typically only produce a 10:1 ratio).
Disadvantages include a tendency for 'wind-up' (a torsional spring rate) in the low torque region.
Strain wave gearing is commonly used in robotics[3] and aerospace.[4] It can provide gear reduction but may also be used to increase rotational speed[citation needed], or for differential gearing.
- ^ Chironis, Nicholas; Sclater, Neil (2007). Mechanisms and Mechanical Devices Sourcebook. ISBN 978-0-07-146761-2.
- ^ Lauletta, Anthony (April 2006). "The Basics of Harmonic Drive Gearing" (PDF). Gear Product News. pp. 32–36. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03.
- ^ Li, Z; Melek, WW; Clark, C (2009). "Decentralized robust control of robot manipulators with harmonic drive transmission and application to modular and reconfigurable serial arms". Robotica. 27 (2): 291–302. doi:10.1017/S0263574708004712.
- ^ Ueura, K; Kiyosawa, Y; Kurogi, J; Kanai, S; Miyaba, H; Maniwa, K; Suzuki, M; Obara, S (2008). "Tribological aspects of a strain wave gearing system with specific reference to its space application". Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology. 222 (8): 1051–1061. doi:10.1243/13506501JET415. ISSN 1350-6501. S2CID 108896120.
Previous Page Next Page


