Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
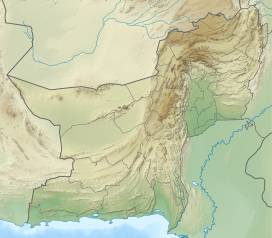
Sulaiman Mountains
| Sulaiman Range | |
|---|---|
| د كسې غرونه / کوه سليمان | |
 Satellite image of a part of the Sulaiman Range | |
| Highest point | |
| Coordinates | 30°30′N 70°10′E / 30.500°N 70.167°E |
| Dimensions | |
| Area | 6,475 km2 (2,500 sq mi)https://dgkhan.punjab.gov.pk/tribal_area |
| Geography | |
| Location | Zabul, Kandahar and Loya Paktia, Afghanistan northern Balochistan, and FATA, Pakistan |
| Parent range | Hindu Kush |
The Sulaiman Mountains, also known as Kōh-e Sulaymān (Balochi:کوهِ سليمان; "Mountains of Prophet Solomon") or Da Kasē Ghrūna (Pashto: د كسې غرونه; "Mountains of Qaes/Kasi"), are a north–south extension of the southern Hindu Kush mountain system in Pakistan and Afghanistan. They are also known as Aparanchal Range, or Western Mountains (Sanskrit: अपरा; romanised: Aparā; literally: "West"; आंचल; romanised: ānchal; literally: "mountains" or "mountainous region"), as they mark the westernmost boundary of the Indian Subcontinent. They rise to form the eastern edge of the Iranian plateau.[1] They are located in the Kandahar, Zabul and Paktia provinces of Afghanistan, and in Pakistan they extend over the northern part of Balochistan and Waziristan as well as Kurram of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. In southwestern Punjab, the mountains extend into the two districts of Dera Ghazi Khan and Rajanpur, which are located west of the Indus River on the boundary with Balochistan. Bordering the mountains to the east are the plains of the Indus River valley, and to the north are the arid highlands of the Central Hindu Kush whose heights extend up to 3,383 metres (11,099 ft).[2] The total area on which this range spans around 6,475 sq. km (2,500 sq mi).[3] Together with the Kirthar Mountains on the border between Balochistan and Sindh, the Sulaiman Mountains form what is known as the Sulaiman-Kirthar geologic province.[4]
The most well-known peak of the Sulaimans is the twin-peaked Takht-e-Sulaiman or "Throne of Prophet Solomon" at 3,487 metres (11,440 ft),[5] located near Darazinda in Dera Ismail Khan Subdivision, close to the border with both South Waziristan and the Zhob District of neighboring Balochistan province. The highest peak, however, is Zarghun Ghar at 3,578 metres (11,739 ft) near Quetta, Pakistan. The next highest peak in Balochistan province is Khilafat Hill at 3,475 metres (11,401 ft), which is located in the Ziarat District of Pakistan and is famous for the Ziarat Juniper Forest, where Juniperus macropoda trees grow.[6]
- ^ Akroyd, Clarissa (2014-11-17). Pakistan. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-1-63355-947-9.
- ^ Khan, Fazle Karim (1991). A Geography of Pakistan: Environment, People and Economy. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-577411-5.
- ^ "Koh-e-Suleman | District Dera Ghazi Khan". dgkhan.punjab.gov.pk. Retrieved 2023-06-06.
- ^ "USGS Bulletin 2208-C: Sembar Goru/Ghazij Composite Total Petroleum System, Indus and Sulaiman-Kirthar Geologic Provinces, Pakistan and India". pubs.usgs.gov. Retrieved 2020-04-20.
- ^ Park, Graham (2017-11-09). Mountains: The origins of the Earth's mountain systems. Dunedin Academic Press Ltd. ISBN 978-1-78046-579-1.
- ^ Shah, Syed Ali (10 July 2013). "In Balochistan, an ancient forest battles for survival". Dawn. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
Previous Page Next Page