Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Teicoplanin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌtaɪkoʊˈpleɪnɪn/ TY-koh-PLAY-nin |
| Trade names | Targocid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, intramuscular |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90% (given IM) |
| Protein binding | 90% to 95% |
| Metabolism | Nil |
| Elimination half-life | 70 to 100 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (97% unchanged) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | Variable |
| Molar mass | 1564.3 to 1907.7 g/mol |
| Melting point | 260 °C (500 °F) (dec.) |
| |
| | |
Teicoplanin is an semisynthetic glycopeptide antibiotic with a spectrum of activity similar to vancomycin. Its mechanism of action is to inhibit bacterial cell wall[3] peptidoglycan[4] synthesis. It is used in the prophylaxis and treatment of serious infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis.[3]
Teicoplanin is widely available in many European, Asian, and South American countries, however it is not currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration and is not commercially available in the United States.[5] Teicoplanin is marketed by Sanofi-Aventis under the trade name Targocid.[6] Other trade names include Ticocin marketed by Cipla(India).[citation needed]
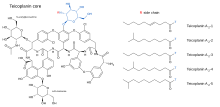
Its strength is considered to be due to the length of the hydrocarbon chain.[7]
- ^ "Prescription medicines: registration of new generic medicines and biosimilar medicines, 2017". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 30 March 2024.
- ^ Human Medicines Evaluation Division (10 December 2020). "Active substance: teicoplanin" (PDF). List of nationally authorised medicinal products. European Medicines Agency.
- ^ a b Reynolds PE (November 1989). "Structure, biochemistry and mechanism of action of glycopeptide antibiotics". European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. 8 (11): 943–950. doi:10.1007/BF01967563. PMID 2532132. S2CID 21551939.
- ^ "Teicoplanin Susceptibility and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Data" (PDF). TOKU-E.
- ^ Murray BE, Arias CA, Nannini EC (2014). Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases (8 ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 377. ISBN 978-1-4557-4801-3.
- ^ Vimberg V (November 2021). "Teicoplanin-A New Use for an Old Drug in the COVID-19 Era?". Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland). 14 (12): 1227. doi:10.3390/ph14121227. PMC 8708781. PMID 34959628.
- ^ Gilpin M, Milner P (1997). "Resisting changes -- Over the past 40 years the glycopeptide antibiotics have played a crucial role in treating bacterial infections. But how long can it continue?". Royal Society of Chemistry. Archived from the original on 2002-12-21. Retrieved 2006-10-15. - includes picture of Teicoplanin's structure.
Previous Page Next Page


