Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Trochlear nerve
| Trochlear nerve | |
|---|---|
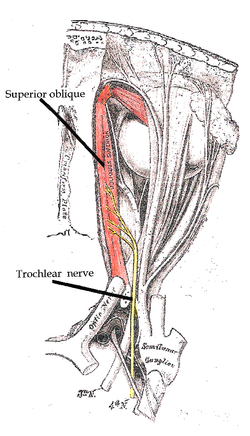 The trochlear nerve entering the orbit, seen from above, supplies the superior oblique muscle | |
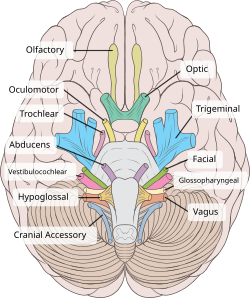 The trochlear nerve (CN IV) seen with other cranial nerves. It is the only cranial nerve to emerge from behind the brainstem, and curves around it to reach the front | |
| Details | |
| Innervates | Superior oblique muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus trochlearis |
| MeSH | D014321 |
| NeuroNames | 466 |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.011 |
| TA2 | 6191 |
| FMA | 50865 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
| Cranial nerves |
|---|
|
The trochlear nerve (/ˈtrɒklɪər/),[1] (lit. pulley-like nerve) also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates a single muscle - the superior oblique muscle of the eye (which operates through the pulley-like trochlea). Unlike most other cranial nerves, the trochlear nerve is exclusively a motor nerve (somatic efferent nerve).
The trochlear nerve is unique among the cranial nerves in several respects:
- It is the smallest nerve in terms of the number of axons it contains.
- It has the greatest intracranial length.
- It is the only cranial nerve that exits from the dorsal (rear) aspect of the brainstem.
- It innervates a muscle, the superior oblique muscle, on the opposite side (contralateral) from its nucleus. The trochlear nerve decussates within the brainstem before emerging on the contralateral side of the brainstem (at the level of the inferior colliculus). An injury to the trochlear nucleus in the brainstem will result in an contralateral superior oblique muscle palsy, whereas an injury to the trochlear nerve (after it has emerged from the brainstem) results in an ipsilateral superior oblique muscle palsy.
The superior oblique muscle which the trochlear nerve innervates ends in a tendon that passes through a fibrous loop, the trochlea, located anteriorly on the medial aspect of the orbit. Trochlea means “pulley” in Latin; the fourth nerve is thus also named after this structure. The words trochlea and trochlear (/ˈtrɒkliə/, /ˈtrɒkliər/) come from Ancient Greek τροχιλέα trokhiléa, “pulley; block-and-tackle equipment”.
- ^ "Trochlear | Definition of Trochlear by Oxford Dictionary on Lexico.com also meaning of Trochlear". Lexico Dictionaries | English. Archived from the original on November 12, 2020.
Previous Page Next Page


