Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Uronic acid

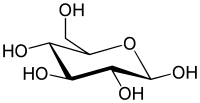

Uronic acids (/ʊˈrɒnɪk/) or alduronic acids are a class of sugar acids with both carbonyl and carboxylic acid functional groups.[1] They are sugars in which the hydroxyl group furthest from the carbonyl group has been oxidized to a carboxylic acid. Usually the sugar is an aldose, but fructuronic acid also occurs. Oxidation of the terminal aldehyde instead yields an aldonic acid, while oxidation of both the terminal hydroxyl group and the aldehyde yields an aldaric acid. The names of uronic acids are generally based on their parent sugars, for example, the uronic acid analog of glucose is glucuronic acid. Uronic acids derived from hexoses are known as hexuronic acids and uronic acids derived from pentoses are known as penturonic acids.[2]
- ^ "Uronic acid". IUPAC Gold Book. 2014. doi:10.1351/goldbook.U06579.
- ^ Mehtiö, Tuomas; Toivari, Mervi; Wiebe, Marilyn G.; Harlin, Ali; Penttilä, Merja; Koivula, Anu (2016). "Production and Applications of Carbohydrate-Derived Sugar Acids as Generic Biobased Chemicals". Critical Reviews in Biotechnology. 36 (5): 904–916. doi:10.3109/07388551.2015.1060189. PMID 26177333. S2CID 6076816.
Previous Page Next Page


