Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Xenon
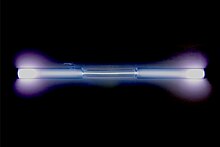 A xenon-filled discharge tube glowing light blue | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Xenon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | colorless gas, exhibiting a blue glow when placed in an electric field | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(Xe) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Xenon in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 54 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 18 (noble gases) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | gas | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 161.40 K (−111.75 °C, −169.15 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 165.051 K (−108.099 °C, −162.578 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density when solid (at t.p.) | 3.408 g/cm3[5] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (at STP) | 5.894 g/L | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at b.p.) | 2.942 g/cm3[6] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Triple point | 161.405 K, 81.77 kPa[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Critical point | 289.733 K, 5.842 MPa[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 2.27 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 12.64 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 21.01[8] J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | common: +2, +4, +6 0,[9] +8[10] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 140±9 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 216 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | face-centered cubic (fcc) (cF4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lattice constant | a = 634.84 pm (at triple point, 161.405 K)[5] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 5.65×10−3 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic[11] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −43.9×10−6 cm3/mol (298 K)[12] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound | gas: 178 m·s−1 liquid: 1090 m/s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-63-3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery and first isolation | William Ramsay and Morris Travers (1898) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of xenon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts.[17] Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized.[18][19][20]
Xenon is used in flash lamps[21] and arc lamps,[22] and as a general anesthetic.[23] The first excimer laser design used a xenon dimer molecule (Xe2) as the lasing medium,[24] and the earliest laser designs used xenon flash lamps as pumps.[25] Xenon is also used to search for hypothetical weakly interacting massive particles[26] and as a propellant for ion thrusters in spacecraft.[27]
Naturally occurring xenon consists of seven stable isotopes and two long-lived radioactive isotopes. More than 40 unstable xenon isotopes undergo radioactive decay, and the isotope ratios of xenon are an important tool for studying the early history of the Solar System.[28] Radioactive xenon-135 is produced by beta decay from iodine-135 (a product of nuclear fission), and is the most significant (and unwanted) neutron absorber in nuclear reactors.[29]
- ^ "xenon". Oxford English Dictionary. Vol. 20 (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. 1989.
- ^ "Xenon". Dictionary.com Unabridged. 2010. Retrieved May 6, 2010.
- ^ "Standard Atomic Weights: Xenon". CIAAW. 1999.
- ^ Prohaska, Thomas; Irrgeher, Johanna; Benefield, Jacqueline; Böhlke, John K.; Chesson, Lesley A.; Coplen, Tyler B.; Ding, Tiping; Dunn, Philip J. H.; Gröning, Manfred; Holden, Norman E.; Meijer, Harro A. J. (May 4, 2022). "Standard atomic weights of the elements 2021 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. doi:10.1515/pac-2019-0603. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ^ a b Arblaster, John W. (2018). Selected Values of the Crystallographic Properties of Elements. Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International. ISBN 978-1-62708-155-9.
- ^ "Xenon". Gas Encyclopedia. Air Liquide. 2009.
- ^ a b Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. p. 4.123. ISBN 1-4398-5511-0.
- ^ Hwang, Shuen-Cheng; Weltmer, William R. (2000). "Helium Group Gases". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Wiley. pp. 343–383. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0701190508230114.a01. ISBN 0-471-23896-1.
- ^ Xe(0) has been observed in tetraxenonogold(II) (AuXe42+).
- ^ Harding, Charlie; Johnson, David Arthur; Janes, Rob (2002). Elements of the p block. Great Britain: Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 93–94. ISBN 0-85404-690-9.
- ^ Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds, in Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (86th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- ^ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.
- ^ Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
- ^ "Observation of two-neutrino double electron capture in 124Xe with XENON1T". Nature. 568 (7753): 532–535. 2019. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1124-4.
- ^ Albert, J. B.; Auger, M.; Auty, D. J.; Barbeau, P. S.; Beauchamp, E.; Beck, D.; Belov, V.; Benitez-Medina, C.; Bonatt, J.; Breidenbach, M.; Brunner, T.; Burenkov, A.; Cao, G. F.; Chambers, C.; Chaves, J.; Cleveland, B.; Cook, S.; Craycraft, A.; Daniels, T.; Danilov, M.; Daugherty, S. J.; Davis, C. G.; Davis, J.; Devoe, R.; Delaquis, S.; Dobi, A.; Dolgolenko, A.; Dolinski, M. J.; Dunford, M.; et al. (2014). "Improved measurement of the 2νββ half-life of 136Xe with the EXO-200 detector". Physical Review C. 89. arXiv:1306.6106. Bibcode:2014PhRvC..89a5502A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.89.015502.
- ^ Redshaw, M.; Wingfield, E.; McDaniel, J.; Myers, E. (2007). "Mass and Double-Beta-Decay Q Value of 136Xe". Physical Review Letters. 98 (5): 53003. Bibcode:2007PhRvL..98e3003R. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.053003.
- ^ "Xenon". Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia (6th ed.). Columbia University Press. 2007. Retrieved October 23, 2007.
- ^ Husted, Robert; Boorman, Mollie (December 15, 2003). "Xenon". Los Alamos National Laboratory, Chemical Division. Retrieved September 26, 2007.
- ^ Rabinovich, Viktor Abramovich; Vasserman, A. A.; Nedostup, V. I.; Veksler, L. S. (1988). Thermophysical properties of neon, argon, krypton, and xenon. National Standard Reference Data Service of the USSR. Vol. 10. Washington, DC: Hemisphere Publishing Corp. Bibcode:1988wdch...10.....R. ISBN 0-89116-675-0.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Cite error: The named reference
beautifulwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
burkewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
mellorwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Sanders, Robert D.; Ma, Daqing; Maze, Mervyn (2005). "Xenon: elemental anaesthesia in clinical practice". British Medical Bulletin. 71 (1): 115–35. doi:10.1093/bmb/ldh034. PMID 15728132.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
basovwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
toyserkaniwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Ball, Philip (May 1, 2002). "Xenon outs WIMPs". Nature. doi:10.1038/news020429-6. Retrieved October 8, 2007.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
saccocciawas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
kaneokawas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
staceywas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
Previous Page Next Page




