Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
ARNr 16S
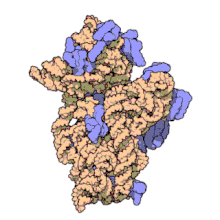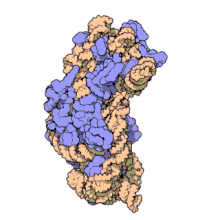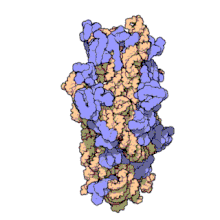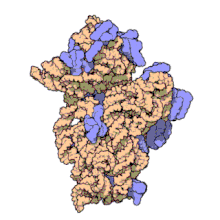
O ARNr 16S, é dicir, ácido ribonucleico ribosómico 16S (en inglés 16S rRNA) é o compoñente da subunidade menor de 30S (S son as unidades svedberg) do ribosoma procariota, o cal se une á secuencia Shine-Dalgarno. Os xenes que o codifican denomínanse xene do ARNr 16S e utilízanse para reconstruír filoxenias, debido ás lentas taxas de evolución desta rexión xénica.[2] Carl Woese e George E. Fox foron os dous investigadores pioneiros no uso do ARNr 16S en filoxenética en 1977.[3]
Nunha soa bacteria poden existir múltiples secuencias do xene de ARNr 16S.[4]
- ↑ Schluenzen F, Tocilj A, Zarivach R, Harms J, Gluehmann M, Janell D, Bashan A, Bartels H, Agmon I, Franceschi F, Yonath A (September 2000). "Structure of functionally activated small ribosomal subunit at 3.3 angstroms resolution". Cell 102 (5): 615–23. PMID 11007480. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00084-2.
- ↑ Woese CR, Fox GE (November 1977). "Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 74 (11): 5088–90. Bibcode:1977PNAS...74.5088W. PMC 432104. PMID 270744. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088.

- ↑ Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML (June 1990). "Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 87 (12): 4576–9. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.4576W. PMC 54159. PMID 2112744. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576.
- ↑ Case RJ, Boucher Y, Dahllöf I, Holmström C, Doolittle WF, Kjelleberg S (January 2007). "Use of 16S rRNA and rpoB genes as molecular markers for microbial ecology studies". Applied and Environmental Microbiology 73 (1): 278–88. PMC 1797146. PMID 17071787. doi:10.1128/AEM.01177-06.
Previous Page Next Page


