Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Absolute value
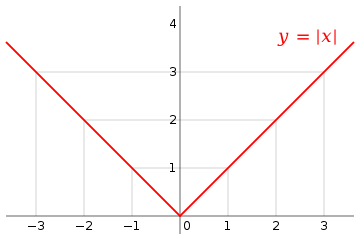
In mathematics, the absolute value of a real number , written as or , is the value of when the sign is dropped (or without its sign).[1][2] That is, for a positive , for a negative , and
For example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of −3 is also 3 (). The absolute value of a real number may be thought of as its distance from zero. It can be defined as follows:
Because a distance is always positive, the absolute value of a number is always positive.
Similarly, the absolute value of a complex number may be thought of as its distance from the origin.
It is defined by the equation[2]
- ↑ "Absolute Value". www.mathsisfun.com. Retrieved 2020-08-28.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weisstein, Eric W. "Absolute Value". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2020-08-28.
Previous Page Next Page











