Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Centriole
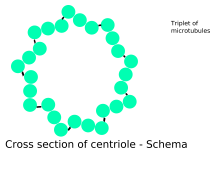

The centriole is a cytoplasmic structure in most eukaryote cells. It is involved in cell division and in the formation of cilia and flagella. Centrioles are not found in vascular plants and in most fungi.[1]
Most centrioles are nine sets of microtubule triplets, arranged in a cylinder. A pair of centrioles, arranged perpendicularly and surrounded by a mass of dense material makes up the centrosome.[2]
- ↑ Quarmby LM & Parker JD (2005). "Cilia and the cell cycle?". The Journal of Cell Biology. 169 (5): 707–710. doi:10.1083/jcb.200503053. PMC 2171619. PMID 15928206. Retrieved 2008-07-08.
- ↑ Eddé B.; et al. (1990). "Posttranslational glutamylation of alpha-tubulin". Science. 247 (4938): 83–85. doi:10.1126/science.1967194. PMID 1967194. Retrieved 2008-07-09.
Previous Page Next Page


