Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Kappa
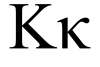 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greek alphabet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Use in other languages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related topics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Kappa (uppercase/lowercase Κ κ) is the letter of the Greek alphabet used to represent the "k" sound in Ancient and Modern Greek. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 20. Letters that came from it include the Roman K and Cyrillic К.
The letter κ always stands for the sound "k" in Greek. It is customary to transliterate (re-write) κ as "c" in English, but this is somewhat problematic since c is pronounced as "s" before e, i and y (which does not happen in Greek).
In mathematics, the lowercase is used to represent the curvature of a curve, while the uppercase Κ is used to represent an ordinal number which is also a cardinal number.[1][2]
- ↑ "Greek/Hebrew/Latin-based Symbols in Mathematics". Math Vault. 2020-03-20. Retrieved 2020-10-06.
- ↑ "Kappa Symbol in Greek Alphabet". www.greeksymbols.net. Retrieved 2020-10-06.
Previous Page Next Page



