Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Magnetic resonance imaging

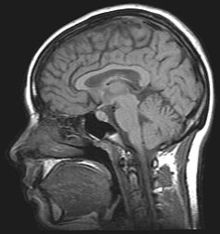

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI), are techniques that doctors use to give a visual representation of soft tissue (flesh) inside the body. Magnetic resonance uses nuclear magnetic resonance to generate these images.
To take an MRI image, the patient lies on a movable bed. The bed enters a strong magnetic field and then radio waves are applied for a short time in a different direction. This sudden shift causes certain atoms in the patient's body to make special signals. The MRI scanner detects those special signals. The MRI scanner then sends the signal information to a computer, and the computer creates an image of the inner body by using the signal information.
Previous Page Next Page
Magnetieseresonansiebeelding AF Imachen por resonancia magnetica AN تصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي Arabic تصوير ب صونيط لمغناطيسي ARY Resonancia magnética nuclear AST Maqnit rezonans tomoqrafiya AZ Магнитно-резонансна томография Bulgarian চৌম্বকীয় অনুরণন প্রতিচ্ছবি Bengali/Bangla Magnetna rezonanca BS Imatge per ressonància magnètica Catalan


