Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Microtubule
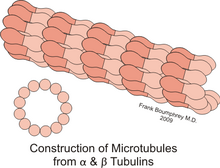
Microtubules are found in biological cells as a part of the cytoskeleton. They are hollow tubes whose walls consist of 13 columns of tubulin molecules. Its main functions are to maintain a cell's shape, cell motility, chromosome movement in cell division, and organelle movement. They look like hollow noodles which transmit signals to our nerves[1][2]
- ↑ Vale RD (Feb 2003). "The molecular motor toolbox for intracellular transport". Cell. 112 (4): 467–80. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00111-9. PMID 12600311. S2CID 15100327.
- ↑ Howard J; Hyman AA (Feb 2007). "Microtubule polymerases and depolymerases". Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 19 (1): 31–5. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2006.12.009. PMID 17184986.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Previous Page Next Page


