Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Normal distribution
Probability density function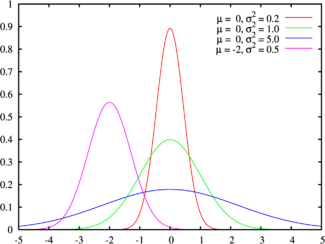 The green line is the standard normal distribution | |
Cumulative distribution function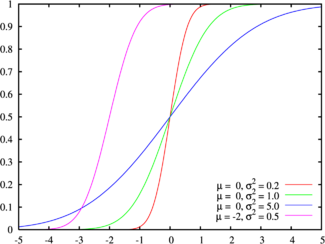 Colors match the image above | |
| Parameters | location (real) squared scale (real) |
|---|---|
| Support | |
| Probability density function (pdf) | |
| Cumulative distribution function (cdf) | |
| Mean | |
| Median | |
| Mode | |
| Variance | |
| Skewness | 0 |
| Excess kurtosis | 0 |
| Entropy | |
| Moment-generating function (mgf) | |
| Characteristic function | |
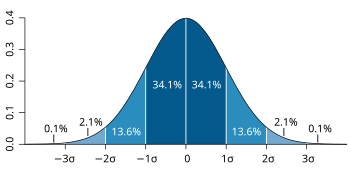
The normal distribution is a probability distribution used in probability theory and statistics. It is also called Gaussian distribution because it was first discovered by Carl Friedrich Gauss. The normal distribution is very important in many fields because many things take this form.[1] A random variable that takes this form is normally distributed, and can be called a normal deviate. The normal distribution is often called the bell curve, because the graph of its probability density looks like a bell. The standard normal distribution (also known as the Z distribution) is a normal distribution that has a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one.[2]
The form of the distribution is
In a normal distribution, the parameter is the mean ("average"). The standard deviation ("variability") is .[2] The variance of the distribution is .
The normal distribution is important because it can represent real-life examples. It is used in natural and social sciences.[3][4] Some examples include:
- Height
- Test scores
- Measurement errors
- Light intensity (as in laser light)
- Insurance companies use normal distributions to model certain average cases.[5]
The central limit theorem can be used to describe real-life data as a normal distribution.[6]
- ↑ "Normal Distribution | Data Basecamp". 2021-11-26. Retrieved 2022-07-15.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "List of Probability and Statistics Symbols". Math Vault. 2020-04-26. Retrieved 2020-08-15.
- ↑ "Normal Distribution - easily explained! | Data Basecamp". 2021-11-26. Retrieved 2023-05-29.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. "Normal Distribution". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2020-08-15.
- ↑ "Normal Distribution". www.mathsisfun.com. Retrieved 2020-08-15.
- ↑ Kwak, Sang Gyu; Kim, Jong Hae (2017-02-21). "Central limit theorem: the cornerstone of modern statistics". National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 2024-05-30.
Previous Page Next Page













