Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Probability distribution
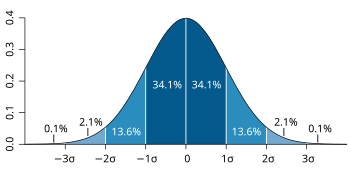
Probability distribution is a term from mathematics. Suppose there are many events with random outcomes. A probability distribution is the theoretical counterpart to the frequency distribution. A frequency distribution simply shows how many times a certain event occurred. A probability distribution says how many times it should have occurred in the long run (that is, its probability). The probability distribution of a random variable is often written as (or simply ).[1][2] Such a distribution can either be discrete, taking a discrete (or countable) amount of values, or continuous, taking an uncountable amount of values (as from a continuous interval).[3]
As an example, the probability distribution for a single roll of a normal 6-sided dice can be presented by:
| Result | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probability of result |
where result is the outcome of the dice roll, and the probability shows the chances of that result occurring. If we roll a dice 60 times, then in the long run, we should expect to have each side appear 10 times on average.
There are different probability distributions.[4] Each of them has its use, its benefits and its drawbacks. Some common probability distributions include:
- Binomial distribution
- Cauchy distribution
- Chi-square distribution
- Exponential distribution
- Gumbel distribution
- Normal distribution
- Poisson distribution
- Student's t-distribution
- ↑ "List of Probability and Statistics Symbols". Math Vault. 2020-04-26. Retrieved 2020-09-11.
- ↑ Bourne, Murray. "11. Probability Distributions - Concepts". www.intmath.com. Retrieved 2020-09-11.
- ↑ "1.3.6.1. What is a Probability Distribution". www.itl.nist.gov. Retrieved 2020-09-11.
- ↑ "Normal Distribution - easily explained! | Data Basecamp". 2021-11-26. Retrieved 2023-05-29.
Previous Page Next Page
توزيع احتمال Arabic Distribución de probabilidá AST Размеркаванне імавернасцей BE Разпределение на вероятностите Bulgarian সম্ভাবনা বিন্যাস Bengali/Bangla Distribució de probabilitat Catalan Rozdělení pravděpodobnosti Czech Пулаяслăхсен валеçĕвĕ CV Dosbarthiad tebygolrwydd CY Wahrscheinlichkeitsverteilung German












