Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Urinary tract infection
| Urinary tract infection | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
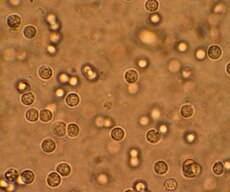 Multiple white cells seen in the urine of a person with a urinary tract infection using a microscope | |
| ICD-10 | N39.0 |
| ICD-9 | 599.0 |
| DiseasesDB | 13657 |
| MedlinePlus | 000521 |
| eMedicine | emerg/625 emerg/626 |
| MeSH | D014552 |
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection caused by bacteria in the urinary tract. The urinary tract is: the kidneys, ureters, the urinary bladder, and urethra. Symptoms of a UTI may be painful peeing, frequent peeing, or wanting to pee (or both). Symptoms of a kidney infection include fever and side and back pain. In older people and young children, the symptoms are not always clear. Often the main cause of a UTI is the bacteria Escherichia coli. Other bacteria, viruses, or fungi may be the cause less often.
Women get urinary tract infections more often than men. Half of women have an infection at some point in their lives. It is common for a person to have many UTI infections in their life. One risk factor for having a UTI is sexual intercourse. Sometimes a person who has a bladder infection will get a kidney infection. Kidney infection may also, but rarely, be caused by bacteria in the blood. Diagnosis in young healthy women can be based on symptoms alone. Sometimes, the urine needs to be tested. A person with frequent infections can take low-dose antibiotics to prevent future infections.
Antibiotics are used to treat simple cases of urinary tract infections. Resistance to antibiotics is increasing. People who have complicated urinary tract infections sometimes have to take antibiotics for a longer time, or might take antibiotics intravenously (through a vein). If symptoms have not improved in two or three days, the person will need further tests. In women, urinary tract infections are the most common form of bacterial infection. 10% of women develop urinary tract infections each year.
Previous Page Next Page


