Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Vietnamese language
| Vietnamese | |
|---|---|
| tiếng Việt | |
| Native to | Vietnam |
Native speakers | 75 million (2007)[1] |
Austroasiatic
| |
| Latin (Vietnamese alphabet) Vietnamese Braille Chữ Nôm (historical) Chữ Hán (historical) | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Association of Southeast Asian Nations |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | vi |
| ISO 639-2 | vie |
| ISO 639-3 | vie |
| Glottolog | viet1252 |
| Linguasphere | 46-EBA |
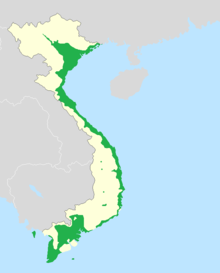 Natively Vietnamese-speaking (non-minority) areas of Vietnam[3] | |
Vietnamese (tiếng Việt) is the official language of Vietnam. Like many other languages in Asia, Vietnamese is a tonal language.
- ↑ Mikael Parkvall, "Världens 100 största språk 2007" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007), in Nationalencyklopedin
- ↑ Citizens belonging to minorities, which traditionally and on long-term basis live within the territory of the Czech Republic, enjoy the right to use their language in communication with authorities and in front of the courts of law (for the list of recognized minorities see National Minorities Policy of the Government of the Czech Republic, Belorussian and Vietnamese since 4 July 2013, see Česko má nové oficiální národnostní menšiny. Vietnamce a Bělorusy). The article 25 of the Czech Charter of Fundamental Rights and Basic Freedoms ensures right of the national and ethnic minorities for education and communication with authorities in their own language. Act No. 500/2004 Coll. (The Administrative Rule) in its paragraph 16 (4) (Procedural Language) ensures, that a citizen of the Czech Republic, who belongs to a national or an ethnic minority, which traditionally and on long-term basis lives within the territory of the Czech Republic, have right to address an administrative agency and proceed before it in the language of the minority. In the case that the administrative agency doesn't have an employee with knowledge of the language, the agency is bound to obtain a translator at the agency's own expense. According to Act No. 273/2001 (About The Rights of Members of Minorities) paragraph 9 (The right to use language of a national minority in dealing with authorities and in front of the courts of law) the same applies for the members of national minorities also in front of the courts of law.
- ↑ From Ethnologue (2009, 2013)
Previous Page Next Page


