Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
2006 Swedish general election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 349 seats in the Riksdag 175 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
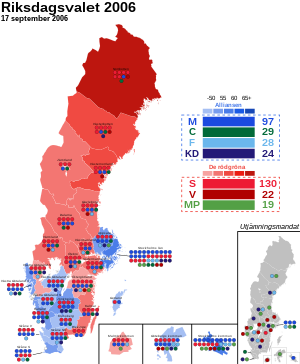
General elections were held in Sweden on 17 September 2006, to elect members to the Riksdag, the Swedish national legislature. All 349 seats were up for election: 310 fixed seats in 29 constituencies and 39 adjustment seats, used to ensure that parties have representation in the Riksdag proportional to their share of the national vote. The electoral system used was semi-open list proportional representation using the Sainte-Laguë method of allocating seats. Elections for County and Municipal councils were also held on the same day.
Fredrik Reinfeldt from the Moderate Party was able to form a majority government together with the Centre Party, Liberal People's Party and the Christian Democrats following the election. The Social Democrats were ousted after twelve years in power. It was the country's first majority government since the second Fälldin cabinet fell in 1981.
Reinfeldt reached out to working-class votes in the re-branding as the 'New Moderates', which resulted in sizeable gains in historically left-wing locations in densely populated areas. As a result, several municipalities that had never voted blue before in Stockholm County flipped.[1] This, combined with a landslide overall win in the capital region as a whole and strong showings in Scania tipped the balance in favour of the Alliance. The centre-right bloc also flipped the crucial populous municipalities Gothenburg, Linköping, Uppsala and Västerås.[1]
The Social Democrats recorded around 35% of the overall support, which was the party's worst showing in the post-war era. Although the red-green parties received a higher proportion of the vote than in the 1991 hung parliament loss, the coalition fell short of a majority by seven seats, or two percentage points of the popular vote.[1]
The Alliance did not reach 50% of the vote, courtesy of several minor parties gathering up 5.67% of the overall vote.[1] This was the final election before the Sweden Democrats entered the Riksdag, with the party getting close to three percent of the vote, falling short by just above one percentage point. The election also saw the party get above 10% in Bjuv Municipality in its Scanian heartlands and above the parliamentary threshold in the country's five southernmost constituencies.[1]
Previous Page Next Page
Eleccions al Parlament de Suècia de 2006 Catalan Parlamentní volby ve Švédsku 2006 Czech Riksdagsvalget i Sverige 2006 Danish Wahl zum Schwedischen Reichstag 2006 German Elecciones generales de Suecia de 2006 Spanish 2006. aasta Rootsi parlamendivalimised ET Ruotsin valtiopäivävaalit 2006 Finnish Élections législatives suédoises de 2006 French Elezioni legislative in Svezia del 2006 Italian Zweedse parlementsverkiezingen 2006 Dutch