Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Aluminium nitride
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
AlN
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.041.931 |
| EC Number |
|
| 13611 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| AlN | |
| Molar mass | 40.989 g/mol[1] |
| Appearance | white to pale-yellow solid |
| Density | 3.255 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 2,500 °C (4,530 °F; 2,770 K)[6] |
| hydrolyses (powder), insoluble (monocrystalline) | |
| Solubility | insoluble, subject of hydrolysis in water solutions of bases and acids [2] |
| Band gap | 6.015 eV[3][4] (direct) |
| Electron mobility | ~300 cm2/(V·s) |
| Thermal conductivity | 321 W/(m·K)[5] |
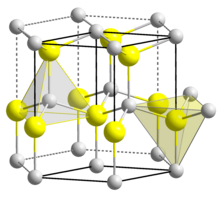
| Structure[7] | |
| Wurtzite | |
| C6v4-P63mc, No. 186, hP4 | |
a = 0.31117 nm, c = 0.49788 nm
| |
Formula units (Z)
|
2 |
| Tetrahedral | |
| Thermochemistry[8] | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
30.1 J/(mol·K) |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
20.2 J/(mol·K) |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−318.0 kJ/mol |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
−287.0 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335, H373, H411 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P271, P280, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Aluminium nitride (AlN) is a solid nitride of aluminium. It has a high thermal conductivity of up to 321 W/(m·K)[5] and is an electrical insulator. Its wurtzite phase (w-AlN) has a band gap of ~6 eV at room temperature and has a potential application in optoelectronics operating at deep ultraviolet frequencies.
- ^ a b Haynes, p. 4.45.
- ^ Fukumoto, S.; Hookabe, T.; Tsubakino, H. (2010). "Hydrolysis behavior of aluminum nitride in various solutions". J. Mat. Science. 35 (11): 2743–2748. doi:10.1023/A:1004718329003. S2CID 91552821.
- ^ Haynes, p. 12.85.
- ^ Feneberg, M.; Leute, R. A. R.; Neuschl, B.; Thonke, K.; Bickermann, M. (2010). Phys. Rev. B. 82 (7): 075208. Bibcode:2010PhRvB..82g5208F. doi:10.1103/physrevb.82.075208.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: untitled periodical (link) - ^ a b Cheng, Zhe; Koh, Yee Rui; Mamun, Abdullah; Shi, Jingjing; Bai, Tingyu; Huynh, Kenny; Yates, Luke; Liu, Zeyu; Li, Ruiyang; Lee, Eungkyu; Liao, Michael E.; Wang, Yekan; Yu, Hsuan Ming; Kushimoto, Maki; Luo, Tengfei; Goorsky, Mark S.; Hopkins, Patrick E.; Amano, Hiroshi; Khan, Asif; Graham, Samuel (2020). "Experimental observation of high intrinsic thermal conductivity of AlN". Physical Review Materials. 4 (4): 044602. arXiv:1911.01595. Bibcode:2020PhRvM...4d4602C. doi:10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.4.044602. S2CID 207780348. Retrieved 2020-04-03.
- ^ Haynes, p. 12.80.
- ^ Vandamme, Nobuko S.; Richard, Sarah M.; Winzer, Stephen R. (1989). "Liquid-Phase Sintering of Aluminum Nitride by Europium Oxide Additives". Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 72 (8): 1409–1414. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1989.tb07662.x.
- ^ Haynes, p. 5.4.
Previous Page Next Page



