Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Caesium sulfide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cesium sulfide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Cs2S | |
| Molar mass | 297.876 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystal |
| Density | 4.19 g·cm−3[1] |
| Melting point | 480 °C[2] |
| Hydrolyzes to form caesium bisulfide[3] | |
| Solubility in ethanol and glycerol | Soluble |
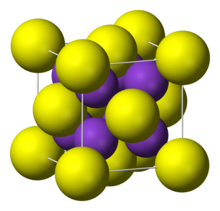
| Structure | |
| cubic, anti-fluorite | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
toxic |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H314, H400 | |
| P260, P264, P273, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Caesium oxide Caesium selenide Caesium telluride Caesium polonide |
Other cations
|
Lithium sulfide Sodium sulfide Potassium sulfide Rubidium sulfide Francium sulfide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cesium sulfide is an inorganic salt with a chemical formula Cs2S. It is a strong alkali in aqueous solution. In the air, cesium sulfide emits rotten egg smelling hydrogen sulfide.
- ^ Sommer, Helmut; Hoppe, Rudolf. The crystal structure of cesium sulfide and a remark about cesium selenide, cesium telluride, rubidium selenide, and rubidium telluride (in German). Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie, 1977. 429: 118-30. ISSN 0044-2313
- ^ Dale L. Perry, Sidney L. Phillips: Handbook of inorganic compounds. CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-8671-8, S. 336 ([1], p. 336, at Google Books).
- ^ Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: Taschenbuch für Chemiker und Physiker. 3. Elemente, anorganische Verbindungen und Materialien, Minerale, Band 3. 4. Auflage, Springer, 1997, ISBN 978-3-5406-0035-0, S. 692 ([2], p. 692, at Google Books).
Previous Page Next Page


