Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Experience curve effects
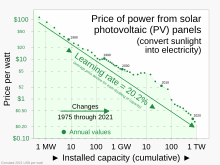
In industry, models of the learning or experience curve effect express the relationship between experience producing a good and the efficiency of that production, specifically, efficiency gains that follow investment in the effort. The effect has large implications for costs[3] and market share, which can increase competitive advantage over time.[4]
- ^ "Solar (photovoltaic) panel prices vs. cumulative capacity". OurWorldInData.org. 2024. Archived from the original on 24 January 2025. OWID credits source data to: Nemet (2009); Farmer & Lafond (2016); International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA, 2024).
- ^ "Swanson's Law and Making US Solar Scale Like Germany". Greentech Media. 2014-11-24.
- ^ Hirschmann, Winfred B. (1964-01-01). "Profit from the Learning Curve". Harvard Business Review. No. January 1964. ISSN 0017-8012. Retrieved 2020-11-17.
- ^ Henderson, Bruce D. "The Experience Curve – Reviewed II: History, 1973". Retrieved 2013-04-05.
Previous Page Next Page


