Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Portal:Physics
The Physics Portal

Physics is the scientific study of matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. A scientist who specializes in the field of physics is called a physicist.
Physics is one of the oldest academic disciplines. Over much of the past two millennia, physics, chemistry, biology, and certain branches of mathematics were a part of natural philosophy, but during the Scientific Revolution in the 17th century, these natural sciences branched into separate research endeavors. Physics intersects with many interdisciplinary areas of research, such as biophysics and quantum chemistry, and the boundaries of physics are not rigidly defined. New ideas in physics often explain the fundamental mechanisms studied by other sciences and suggest new avenues of research in these and other academic disciplines such as mathematics and philosophy.
Advances in physics often enable new technologies. For example, advances in the understanding of electromagnetism, solid-state physics, and nuclear physics led directly to the development of technologies that have transformed modern society, such as television, computers, domestic appliances, and nuclear weapons; advances in thermodynamics led to the development of industrialization; and advances in mechanics inspired the development of calculus. (Full article...)
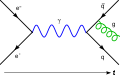
The Smyth Report (officially Atomic Energy for Military Purposes) is the common name of an administrative history written by American physicist Henry DeWolf Smyth about the Manhattan Project, the Allied effort to develop atomic bombs during World War II. The subtitle of the report is A General Account of the Development of Methods of Using Atomic Energy for Military Purposes. It was released to the public on August 12, 1945, just days after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki on August 6 and 9.
Smyth was commissioned to write the report by Major General Leslie R. Groves, Jr., the director of the Manhattan Project. The Smyth Report was the first official account of the development of the atomic bombs and the basic physical processes behind them. It also served as an indication as to what information was declassified; anything in the Smyth Report could be discussed openly. For this reason, the Smyth Report focused heavily on information, such as basic nuclear physics, which was either already widely known in the scientific community or easily deducible by a competent scientist, and omitted details about chemistry, metallurgy, and ordnance. This would ultimately give a false impression that the Manhattan Project was all about physics. (Full article...)
Did you know -
- ... that nuclear fusion reactions are probably occurring at or above the sun's photosphere; it is a process called solar surface fusion.
- ... that the submarine telescope ANTARES, intended to detect neutrinos, may also be used to observe bioluminescent plankton and fish?
- ... that a touch flash releases about a billion photons a second far less than produced in a particle accelerator?
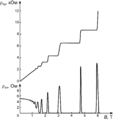
Selected image -
Difference between classical and modern physics

While physics aims to discover universal laws, its theories lie in explicit domains of applicability. Loosely speaking, the laws of classical physics accurately describe systems whose important length scales are greater than the atomic scale and whose motions are much slower than the speed of light. Outside of this domain, observations do not match their predictions. Albert Einstein contributed the framework of special relativity, which replaced notions of absolute time and space with spacetime and allowed an accurate description of systems whose components have speeds approaching the speed of light. Max Planck, Erwin Schrödinger, and others introduced quantum mechanics, a probabilistic notion of particles and interactions that allowed an accurate description of atomic and subatomic scales. Later, quantum field theory unified quantum mechanics and special relativity. General relativity allowed for a dynamical, curved spacetime, with which highly massive systems and the large-scale structure of the universe can be well-described. General relativity has not yet been unified with the other fundamental descriptions; several candidate theories of quantum gravity are being developed.
Related portals
January anniversaries
1 January
- 1894 - Satyendra Nath Bose's birthday.
- 1801 - Giuseppe Piazzi is the first to notice the dwarf planet Ceres. However, very soon astronomers lose sight of its orbital path. After some months, Giuseppe Piazzi finally calculates its correct position on December 31.
- 1985 - Ernie Wise, a comedian, places the first mobile phone call in the UK.
2 January
- 2 January 1822 - Rudolf Clausius was born.
8 January
- 8 January 1942 - Stephen Hawking was born, on the same day that Galileo Galilei died in 1642.
15 January
- 15 January 1908 - Edward Teller was born.
General images
Categories

Fundamentals: Concepts in physics | Constants | Physical quantities | Units of measure | Mass | Length | Time | Space | Energy | Matter | Force | Gravity | Electricity | Magnetism | Waves
Basic physics: Mechanics | Electromagnetism | Statistical mechanics | Thermodynamics | Quantum mechanics | Theory of relativity | Optics | Acoustics
Specific fields: Acoustics | Astrophysics | Atomic physics | Molecular physics | Optical physics | Computational physics | Condensed matter physics | Nuclear physics | Particle physics | Plasma physics
Tools: Detectors | Interferometry | Measurement | Radiometry | Spectroscopy | Transducers
Background: Physicists | History of physics | Philosophy of physics | Physics education | Physics journals | Physics organizations
Other: Physics in fiction | Physics lists | Physics software | Physics stubs
Physics topics
Classical physics traditionally includes the fields of mechanics, optics, electricity, magnetism, acoustics and thermodynamics. The term Modern physics is normally used for fields which rely heavily on quantum theory, including quantum mechanics, atomic physics, nuclear physics, particle physics and condensed matter physics. General and special relativity are usually considered to be part of modern physics as well.
More recognized content
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Sources
Portals on Wikipedia
Previous Page Next Page