Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Southern Zone Sea
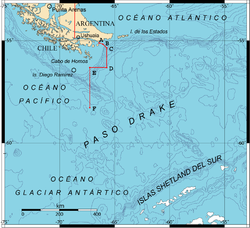
The Sea of the Southern Zone (Spanish: Mar de la Zona Austral)[1] or Southern Zone Sea is the name given by Argentina and Chile to the maritime area whose boundaries were undefined, located south of the Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego. This maritime space was subject to delimitation in the Treaty of Peace and Friendship of 1984 between Chile and Argentina, which ended the Beagle conflict or "Southern Zone conflict."
The definition of this maritime area was constrained by the necessity for the parties ratifying the treaty to avoid referring to the area under delimitation as part of either the Atlantic Ocean or the Pacific Ocean, since the two countries could not agree on its affiliation to one ocean or the other. After the signing of the treaty in 1984 and its ratification in 1985, the name "Sea of the Southern Zone" has been largely ignored in both countries, which continue to use their traditional names in cartographic representations of the area. For this reason, parts of this sea are sometimes linked to the Argentine Sea, Chilean Sea or the Drake Passage.
The name "Sea of the Southern Zone" has not been adopted internationally, and the International Hydrographic Organization did not include the Sea of the Southern Zone in the draft of the 4th edition of its publication Limits of Oceans and Seas, issued via Circular CL55 of 7 November 2001 (the 3rd edition dates from 1953).[2] In this draft, Chile, in agreement with Russia and the United Kingdom, proposed as the northern limit of the Drake Passage the line connecting Waterman Island, Cape Horn, Cape San Bartolomé on Isla de los Estados, and the southern coast of that island to Cape San Juan de Salvamento, clearly overlapping areas under the delimitation of the Sea of the Southern Zone.[3]
- ^ The 1984 Treaty says about the maritime border: Artículo 7°. El límite entre las respectivas soberanías sobre el mar, suelo y subsuelo de la República Argentina y de la República de Chile en el Mar de la Zona Austral a partir del término de la delimitación existente en el Canal Beagle,...
- ^ Circular CL55 of 2001
- ^ Map of the proposed limits for the Drake Passage submitted to the IHO
Previous Page Next Page


