Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Tungsten diselenide
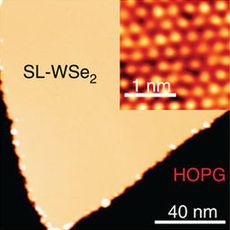 WSe2 monolayer on graphene (yellow) and its atomic image (inset)[1]
| |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.877 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| WSe2 | |
| Molar mass | 341.76 g/mol |
| Appearance | grey to black solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 9.32 g/cm3[2] |
| Melting point | > 1200 °C |
| insoluble | |
| Band gap | ~1 eV (indirect, bulk)[3] ~1.7 eV (direct, monolayer)[4] |
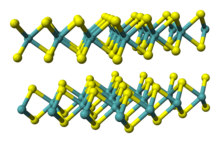
| Structure | |
| hP6, space group P6 3/mmc, No 194[2] | |
a = 0.3297 nm, c = 1.2982 nm
| |
| Trigonal prismatic (WIV) Pyramidal (Se2−) | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-185.3 kJ mol−1[5] |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Tantalum diselenide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tungsten diselenide is an inorganic compound with the formula WSe2.[6] The compound adopts a hexagonal crystalline structure similar to molybdenum disulfide. The tungsten atoms are covalently bonded to six selenium ligands in a trigonal prismatic coordination sphere while each selenium is bonded to three tungsten atoms in a pyramidal geometry. The tungsten–selenium bond has a length of 0.2526 nm, and the distance between selenium atoms is 0.334 nm.[7] It is a well studied example of a layered material. The layers stack together via van der Waals interactions. WSe2 is a very stable semiconductor in the group-VI transition metal dichalcogenides.
- ^ Chiu, Ming-Hui; Zhang, Chendong; Shiu, Hung-Wei; Chuu, Chih-Piao; Chen, Chang-Hsiao; Chang, Chih-Yuan S.; Chen, Chia-Hao; Chou, Mei-Yin; Shih, Chih-Kang; Li, Lain-Jong (2015). "Determination of band alignment in the single-layer MoS2/WSe2 heterojunction". Nature Communications. 6: 7666. arXiv:1406.5137. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.7666C. doi:10.1038/ncomms8666. PMC 4518320. PMID 26179885.
- ^ a b Agarwal, M. K.; Wani, P. A. (1979). "Growth conditions and crystal structure parameters of layer compounds in the series Mo1−xWxSe2". Materials Research Bulletin. 14 (6): 825–830. doi:10.1016/0025-5408(79)90144-2.
- ^ Prakash, Abhijith; Appenzeller, Joerg (2017-02-28). "Bandgap Extraction and Device Analysis of Ionic Liquid Gated WSe2 Schottky Barrier Transistors". ACS Nano. 11 (2): 1626–1632. doi:10.1021/acsnano.6b07360. ISSN 1936-0851. PMID 28191930.
- ^ Yun, Won Seok; Han, S. W.; Hong, Soon Cheol; Kim, In Gee; Lee, J. D. (2012). "Thickness and strain effects on electronic structures of transition metal dichalcogenides: 2H-MX2 semiconductors (M = Mo, W; X = S, Se, Te)". Physical Review B. 85 (3): 033305. Bibcode:2012PhRvB..85c3305Y. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.85.033305.
- ^ O'Hare, P.A.G.; Lewis, Brett M.; parkinson, B.A. (June 1988). "Standard molar enthalpy of formation by fluorine-combustion calorimetry of tungsten diselenide (WSe2). Thermodynamics of the high-temperature vaporization of WSe2. Revised value of the standard molar enthalpy of formation of molybdenite (MoS2)". The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. 20 (6): 681–691. doi:10.1016/0021-9614(88)90019-5.
- ^ Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- ^ Schutte, W.J.; De Boer, J.L.; Jellinek, F. (1986). "Crystal Structures of Tungsten Disulfide and Diselenide". Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 70 (2): 207–209. Bibcode:1987JSSCh..70..207S. doi:10.1016/0022-4596(87)90057-0.
Previous Page Next Page


