Back Baghdad ACE Багдад ADY Bagdad AF Bagdad ALS ባግዳድ AM Bagdad AN بغداد Arabic ܒܓܕܐܕ (ܡܕܝܢܬܐ) ARC بغداد ARY بغداد ARZ
Baghdad
بَغْدَاد | |
|---|---|
| Mayoralty of Baghdad | |
Top-bottom, L-R: Aerial view of the Green Zone; Haydar-Khana Mosque • Statue of Karim Qasim Iraq Museum • House of Sassoon Eskell Atraqchi for Art & cultural heritage • View over Baghdad and the Tigris river | |
| Nickname: City of Peace (مَدِيْنَةُ السَّلَام)[1] | |
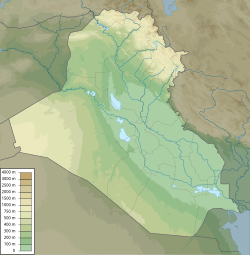
| Coordinates: 33°18′55″N 44°21′58″E / 33.31528°N 44.36611°E | |
| Country | Iraq |
| Governorate | Baghdad |
| Established | 30 July 762 AD |
| Founded by | Caliph al-Mansur |
| Districts | 11 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–council |
| • Body | Baghdad City Advisory Council |
| • Mayor | Ammar Moussa Kadhum |
| Area | |
| 673 km2 (260 sq mi) | |
| Elevation | 34 m (112 ft) |
| Population | |
• Estimate (2024) | 7,921,134[2] |
| • Rank | 1st in Iraq |
| • Density | 12,000/km2 (30,000/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 8,141,000 |
| Demonym | Baghdadi |
| Time zone | UTC+03:00 (Arabian Standard Time) |
| • Summer (DST) | (Not Observed) |
| Postal code | 10001 to 10090 |
| Website | amanatbaghdad.gov.iq (in Arabic) |
Baghdad[note 1] (Arabic: بغداد, Baghdād) is the capital and largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the most populous cities in the Middle East and Arab World and forms 22% of the country's population. Spanning an area of approximately 673 square kilometres (260 sq mi), Baghdad is the capital of the Baghdad Governorate and serves as Iraq's political, economic, and cultural hub.
Founded in 762 AD by Al-Mansur, Baghdad was the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate and became its most notable development project. The city evolved into a cultural and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multi-ethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning". For much of the Abbasid era, during the Islamic Golden Age, Baghdad was one of the largest cities in the world (rivals Chang'an), as the population peaked at more than one million. It was largely destroyed at the hands of the Mongol Empire in 1258, resulting in a decline that would linger through many centuries due to frequent plagues and multiple successive empires.
The city was part of the Ottoman Empire's Baghdad Vilayet until World War I, when it was captured by British forces. Baghdad became the capital of the former British Mandate of Mesopotamia in 1921. With the recognition of Iraq as an independent monarchy in 1932, it gradually regained some of its former prominence as a significant center of Arab culture. During the oil boom in Iraq, the city experienced a period of prosperity and growth. It faced severe infrastructural damage due to the Iraq War, which began with the 2003 invasion of Iraq, resulting in a substantial loss of cultural heritage and historical artifacts. Impacted by the subsequent insurgency and renewed war, during this period, it had one of the highest rates of terrorist attacks in the world. However, terrorist attacks have gradually been on the decline since the territorial defeat of the Islamic State militant group in Iraq in 2017, and are very rare now.
As capital of Iraq, Baghdad is location of the seat of government, national institutions and government ministries and serves as headquarters to numerous companies. It generates 40% of Iraq's GDP. A major center of Islamic history, it is home to numerous historic mosques, as well as a large number of churches, mandis and synagogues, highlighting the city's historical diversity. Baghdad is home to Mustansiriya University, one of the oldest universities and Masjid al-Kādhimayn is visited every year by millions of Shi'ite pilgrims. The city is home to important cultural sites such as the National Museum of Iraq, the Iraqi National Library and the National Media Center. It is also known as the "City of Palaces", as it is home to well known palaces.
- ^ Petersen, Andrew (13 September 2011). "Baghdad (Madinat al-Salam)". Islamic Arts & Architecture. Archived from the original on 16 September 2016. Retrieved 23 August 2016.
- ^ "Baghdad Population Live". Retrieved 16 May 2024.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).