
Back مكلورثامين Arabic مکلورتامین AZB Clormethin CY Mechlorethamin German Mecloretamina Spanish مکلورتامین FA Bis(2-kloorietyyli)metyyliamiini Finnish Chlorméthine French Mecloretamina Italian メクロレタミン Japanese
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
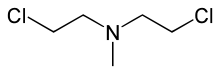
2-Chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylethanamine
| |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.110 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Mechlorethamine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2810 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H11Cl2N | |
| Molar mass | 156.05 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Fishy, ammoniacal |
| log P | 0.91 |
| Pharmacology | |
| D08AX04 (WHO) L01AA05 (WHO) | |
| |
| |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| <1 minute | |
| 50% (Kidney) | |
| Legal status | |
| Related compounds | |
Related amines
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chlormethine (INN, BAN), also known as mechlorethamine (USAN, USP), mustine, HN2, and (in post-Soviet states) embikhin (эмбихин), is a nitrogen mustard sold under the brand name Mustargen among others. It is the prototype of alkylating agents, a group of anticancer chemotherapeutic drugs. It works by binding to DNA, crosslinking two strands and preventing cell duplication. It binds to the N7 nitrogen on the DNA base guanine. As the chemical is a blister agent, its use is strongly restricted within the Chemical Weapons Convention where it is classified as a Schedule 1 substance.
Mechlorethamine belongs to the group of nitrogen mustard alkylating agents.[4][5][6]
- ^ a b c "Ledaga". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 30 June 2021. Archived from the original on 5 September 2021. Retrieved 5 September 2021.
- ^ a b "Ledaga EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 5 September 2021. Retrieved 5 September 2021.
- ^ "Health product highlights 2021: Annexes of products approved in 2021". Health Canada. 3 August 2022. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- ^ Rappeneau S, Baeza-Squiban A, Jeulin C, Marano F (March 2000). "Protection from cytotoxic effects induced by the nitrogen mustard mechlorethamine on human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro". Toxicol. Sci. 54 (1): 212–21. doi:10.1093/toxsci/54.1.212. PMID 10746948.
- ^ "Chapter 3: Principles of Oncologic Pharmacotherapy". Cancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach. 2010. Archived from the original on 15 May 2009. Retrieved 8 October 2023.
- ^ "CDC - The Emergency Response Safety and Health Database: Blister Agent: NITROGEN MUSTARD HN-2 - NIOSH". U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Archived from the original on 2019-06-28. Retrieved 2016-04-20.