Back مترو دلهي Arabic دهلی متروسو AZB Метрапалітэн Дэлі BE দিল্লি মেট্রো Bengali/Bangla দিল্লী মেট্রো BPY Metro de Nova Delhi Catalan Metro v Dillí Czech Metro Delhi German Μετρό Δελχί Greek Metroo de Delhio EO
| Delhi Metro | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
 A Yellow Line train at Patel Chowk metro station | |||
| Overview | |||
| Owner | Delhi Metro Rail Corporation | ||
| Locale | National Capital Region (NCR) | ||
| Transit type | Rapid transit | ||
| Number of lines | 10[1] | ||
| Line number | |||
| Number of stations | 256[a] | ||
| Daily ridership | 46.26 lakh (4.62 million, 2022–23)[2] | ||
| Annual ridership | 203 crore (2.03 billion, 2023)[b][3] | ||
| Key people | Manoj Joshi (chairman) Vikas Kumar (managing director)[4] | ||
| Headquarters | Metro Bhawan, Barakhamba Road, New Delhi | ||
| Website | delhimetrorail.com | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 24 December 2002 | ||
| Operator(s) | Delhi Metro Rail Corporation | ||
| Number of vehicles | 336 trains[5] | ||
| Train length | 4/6/8 coaches[6] | ||
| Headway | 3 minutes | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 350.42 km (217.74 mi)[c] | ||
| Track gauge |
| ||
| Electrification | 25 kV 50 Hz AC overhead catenary | ||
| Average speed | 45 km/h[7][8] | ||
| Top speed | 120 km/h[9][8] | ||
| |||
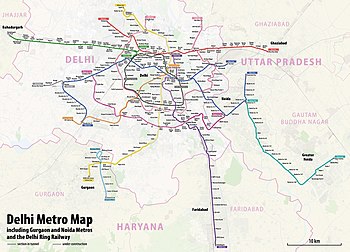
The Delhi Metro is a rapid transit system that serves Delhi and the adjoining satellite cities of Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurugram, Noida, Bahadurgarh, and Ballabhgarh in the National Capital Region of India.[10] The system consists of 10 colour-coded lines[1] serving 256 stations,[a] with a total length of 350.42 kilometres (217.74 mi).[c] It is India's largest and busiest metro rail system and the second-oldest, after the Kolkata Metro. The metro has a mix of underground, at-grade, and elevated stations using broad-gauge and standard-gauge tracks. The metro makes over 4,300 trips daily.[12]
Construction began in 1998, and the first elevated section (Shahdara to Tis Hazari) on the Red Line opened on 25 December 2002. The first underground section (Vishwa Vidyalaya – Kashmere Gate) on the Yellow Line opened on 20 December 2004.[13] The network was developed in phases. Phase I was completed by 2006, followed by Phase II in 2011. Phase III was mostly complete in 2021, except for a small extension of the Airport Line which opened in 2023.[14] Construction of Phase IV began on 30 December 2019.[15]
The Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC), a joint venture between the Government of India and Delhi, built and operates the Delhi Metro.[16][17] The DMRC was certified by the United Nations in 2011 as the first metro rail and rail-based system in the world to receive carbon credits for reducing greenhouse-gas emissions, reducing annual carbon emission levels in the city by 630,000 tonnes.[6]
The Delhi Metro has interchanges with the Rapid Metro Gurgaon (with a shared ticketing system) and Noida Metro. On 22 October 2019, DMRC took over operations of the financially-troubled Rapid Metro Gurgaon.[18] The Delhi Metro's annual ridership was 203.23 crore (2.03 billion) in 2023.[b][19][20] The system will have interchanges with the Delhi-Meerut RRTS, India's fastest urban regional transit system.[21][22]
- ^ a b c "Present Network". www.delhimetrorail.com. Retrieved 16 April 2022.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Economic Survey of Delhi 2023–24was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Gandhiok, Jasjeev (18 January 2024). "Delhi Metro logs 2 billion passenger trips for 2023 — highest ever". Hindustan Times. New Delhi. Retrieved 19 January 2024.
- ^ "Board of Directors of DMRC". www.delhimetrorail.com. Retrieved 2 April 2022.
- ^ "Delhi Metro adding 120 more coaches to upgrade remaining fleet of 6-coach trains". Hindustan Times. 4 April 2021. Retrieved 10 April 2022.
- ^ a b c d "Introduction | DMRC". www.delhimetrorail.com. Retrieved 16 April 2022.
- ^ "VROOM! Delhi metro top speed increased! Now, IGI Airport to New Delhi Railway Station in just". 22 March 2023.
- ^ a b "Delhi airport metro line, now running at 100 KMPH". 23 March 2023.
- ^ "Delhi Metro increases speed to 120 kmph on Airport Line. Know how long will it take to reach Delhi airport". Live Mint. 16 September 2023.
- ^ Dua, Tanya (24 November 2018). "After 5 years of riding the New York City subway, I tried the Delhi Metro at the busiest time of the year – and it showed me exactly what I'm missing". Business Insider. Retrieved 24 February 2019.
- ^ a b "Route map". www.delhimetrorail.com. Retrieved 16 April 2022.
- ^ "DMRC Services Update". delhimetrorail.com. Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC). 24 October 2023. Retrieved 14 November 2023.
- ^ Roy, Sidharatha (25 December 2017). "Delhi Metro: It all started 15 Xmas days ago". The Times of India. New Delhi. Archived from the original on 7 January 2018. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- ^ "DMRC's remarkable growth: Delhi Metro surpasses 390 kms, becomes India's longest metro network". 18 September 2023.
- ^ "Project Update an Janakpuri West – R. K. Ashram Marg corridor".
- ^ "Delhi Metro to join global club of metro networks having span of over 300 km". The Times of India. 29 October 2018.
- ^ "PM inaugurates KMP expressway, Ballabhgarh-Mujesar Metro rail link".
- ^ "Delhi Metro takes over operations of Gurgaon Rapid Metro". mint. 23 October 2019. Retrieved 16 April 2022.
- ^ Gandhiok, Jasjeev (18 January 2024). "Delhi Metro logs 2 billion passenger trips for 2023 — highest ever". Hindustan Times. New Delhi. Retrieved 19 January 2024.
- ^ Ashish Chandrorkar (19 February 2021). "A comprehensive report on Metro rail systems in India" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 31 August 2021.
- ^ "Project Overview - NCRTC". ncrtc.in. NCRTC. Retrieved 14 November 2023.
- ^ "Delhi – Meerut RRTS – Information, Route Map, Fares, Tenders & Updates". themetrorailguy.com. The Metro Rail Guy. Retrieved 14 November 2023.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).