
Back Elektrofilní halogenace Czech Halogenación electrofílica Spanish هالوژندار کردن الکتروندوستی FA Halogénation électrophile aromatique French Aromás elektrofil halogénezés Hungarian Aromatische halogenering Dutch Halogenação eletrofílica Portuguese
In organic chemistry, an electrophilic aromatic halogenation is a type of electrophilic aromatic substitution. This organic reaction is typical of aromatic compounds and a very useful method for adding substituents to an aromatic system.
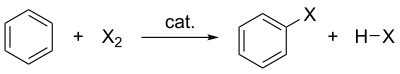
Halogenation of benzene where X is the halogen, catalyst represents the catalyst (if needed) and HX represents the protonated base.
A few types of aromatic compounds, such as phenol, will react without a catalyst, but for typical benzene derivatives with less reactive substrates, a Lewis acid is required as a catalyst. Typical Lewis acid catalysts include AlCl3, FeCl3, FeBr3 and ZnCl2. These work by forming a highly electrophilic complex which is attacked by the benzene ring.
