
Back এক্সপেরিমেন্টাল এডভান্সড সুপারকন্ডাক্টিং টোকামাক Bengali/Bangla Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak German Tokamak Superconductor Experimental Avanzado Spanish توکاماک ابررسانای تجربی پیشرفته FA Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak French Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak Italian EAST Korean एक्सपेरिमेन्टल एडभान्स्ड सुपरकन्डक्टिङ टोकामक NE EAST Dutch EAST Russian
| Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak | |
|---|---|
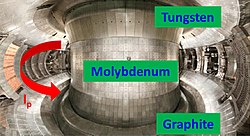 EAST vacuum vessel | |
| Device type | Tokamak |
| Location | Hefei, China |
| Affiliation | Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| Technical specifications | |
| Major radius | 1.85 m (6 ft 1 in) |
| Minor radius | 0.45 m (1 ft 6 in) |
| Magnetic field | 3.5 T (35,000 G) |
| Heating power | 7.5 MW |
| Discharge duration | 102 s |
| Plasma current | 1.0 MA |
| Plasma temperature | 100×106 K |
| History | |
| Year(s) of operation | 2006–present |
| Preceded by | HT-6M |
| Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 先进超导托卡马克实验装置 | ||||||
| Hanyu Pinyin | xiānjìn chāodǎo tuōkǎmǎkè shíyàn zhuāngzhì | ||||||
| Literal meaning | Advanced Superconducting Tokamak Experimental device | ||||||
| |||||||

The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), also known as HT-7U (Hefei Tokamak 7 Upgrade), is an experimental superconducting tokamak magnetic fusion energy reactor in Hefei, China. Operated by the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science conducting its experiments for the Chinese Academy of Sciences, EAST began its operations in 2006. EAST is part of the international ITER program after China joined the initiative in 2003[1] and acts as a testbed for ITER technologies.[2] On January 20, 2025, it sustained plasma for 1066 seconds.[3]
It is the first tokamak to utilize superconducting toroidal and poloidal magnets.
- ^ "China's New Thermonuclear Fusion Reactor Test Successful -- china.org.cn". www.china.org.cn. Retrieved 2024-12-03.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:0was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
livesciencewas invoked but never defined (see the help page).