
Back عمارة مستقبلية Arabic Futuristička arhitektura BS Arquitectura futurista Spanish Arquitetura huturista EXT معماری آیندهگرا FA Architecture futuriste French אדריכלות עתידנית (פוטוריסטית) HE Futurista építészet Hungarian Architettura futurista Italian Футуристичка архитектура MK
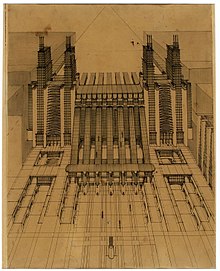
Futurist architecture is an early-20th century form of architecture born in Italy, characterized by long dynamic lines, suggesting speed, motion, urgency and lyricism: it was a part of Futurism, an artistic movement founded by the poet Filippo Tommaso Marinetti, who produced its first manifesto, the Manifesto of Futurism, in 1909. The movement attracted not only poets, musicians, and artists (such as Umberto Boccioni, Giacomo Balla, Fortunato Depero, and Enrico Prampolini) but also a number of architects. A cult of the Machine Age and even a glorification of war and violence were among the themes of the Futurists - several prominent futurists were killed after volunteering to fight in World War I. The latter group included the architect Antonio Sant'Elia, who, though building little, translated the futurist vision into an urban form.[1]
- ^ Günter Berghaus (2000). International Futurism in Arts and Literature. Walter de Gruyter. p. 364. ISBN 3-11-015681-4.