This article may rely excessively on sources too closely associated with the subject, potentially preventing the article from being verifiable and neutral. (August 2023) |
| Original author(s) | OpenAI |
|---|---|
| Initial release | June 2018 |
| Repository | |
| Successor | GPT-2 |
| Type | |
| License | MIT[1] |
| Website | openai |
| Part of a series on |
| Machine learning and data mining |
|---|
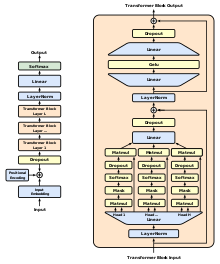
Generative Pre-trained Transformer 1 (GPT-1) was the first of OpenAI's large language models following Google's invention of the transformer architecture in 2017.[2] In June 2018, OpenAI released a paper entitled "Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training",[3] in which they introduced that initial model along with the general concept of a generative pre-trained transformer.[4]
Up to that point, the best-performing neural NLP models primarily employed supervised learning from large amounts of manually labeled data. This reliance on supervised learning limited their use of datasets that were not well-annotated, in addition to making it prohibitively expensive and time-consuming to train extremely large models;[3][5] many languages (such as Swahili or Haitian Creole) are difficult to translate and interpret using such models due to a lack of available text for corpus-building.[5] In contrast, a GPT's "semi-supervised" approach involved two stages: an unsupervised generative "pre-training" stage in which a language modeling objective was used to set initial parameters, and a supervised discriminative "fine-tuning" stage in which these parameters were adapted to a target task.[3]
The use of a transformer architecture, as opposed to previous techniques involving attention-augmented RNNs, provided GPT models with a more structured memory than could be achieved through recurrent mechanisms; this resulted in "robust transfer performance across diverse tasks".[3]
- ^ "gpt-2". GitHub. Archived from the original on 11 March 2023. Retrieved 13 March 2023.
- ^ Vaswani, Ashish; Shazeer, Noam; Parmar, Niki; Uszkoreit, Jakob; Jones, Llion; Gomez, Aidan N; Kaiser, Łukasz; Polosukhin, Illia (2017). "Attention is All you Need" (PDF). Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 30. Curran Associates, Inc.
- ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
gpt1paperwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "GPT-1 to GPT-4: Each of OpenAI's GPT Models Explained and Compared". 11 April 2023. Archived from the original on 2023-04-15. Retrieved 2023-04-29.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
tsvetkovwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
