
Back Dikderm AF Dickdarm ALS Bodiello gordo AN Nkat ile ANN أمعاء غليظة Arabic ܡܥܝܐ ܥܒܝܐ ARC বৃহদান্ত্ৰ AS Intestín gordu AST Yoğun bağırsaq AZ یوغون باغیرساق AZB
| Large intestine | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Gastrointestinal tract |
| System | Digestive system |
| Artery | Superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric and iliac arteries |
| Vein | Superior and inferior mesenteric vein |
| Lymph | Inferior mesenteric lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | colon or intestinum crassum |
| MeSH | D007420 |
| TA98 | A05.7.01.001 |
| TA2 | 2963 |
| FMA | 7201 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
 |
| Major parts of the |
| Gastrointestinal tract |
|---|
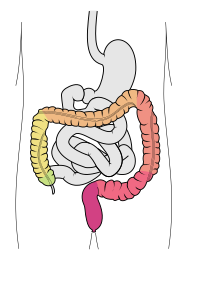
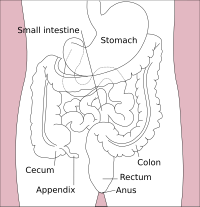
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being removed by defecation.[1] The colon (progressing from the ascending colon to the transverse, the descending and finally the sigmoid colon) is the longest portion of the large intestine, and the terms "large intestine" and "colon" are often used interchangeably, but most sources define the large intestine as the combination of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal.[1][2][3] Some other sources exclude the anal canal.[4][5][6]
In humans, the large intestine begins in the right iliac region of the pelvis, just at or below the waist, where it is joined to the end of the small intestine at the cecum, via the ileocecal valve. It then continues as the colon ascending the abdomen, across the width of the abdominal cavity as the transverse colon, and then descending to the rectum and its endpoint at the anal canal.[7] Overall, in humans, the large intestine is about 1.5 metres (5 ft) long, which is about one-fifth of the whole length of the human gastrointestinal tract.[8]
- ^ a b "large intestine". NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health. 2011-02-02. Retrieved 2014-03-04.
- ^ Kapoor, Vinay Kumar (13 Jul 2011). Gest, Thomas R. (ed.). "Large Intestine Anatomy". Medscape. WebMD LLC. Retrieved 2013-08-20.
- ^ Gray, Henry (1918). Gray's Anatomy. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.
- ^ "large intestine". Mosby's Medical Dictionary (8th ed.). Elsevier. 2009. ISBN 9780323052900.
- ^ "intestine". Concise Medical Dictionary. Oxford University Press. 2010. ISBN 9780199557141.
- ^ "large intestine". A Dictionary of Biology. Oxford University Press. 2013. ISBN 9780199204625.
- ^ "Large intestine". Archived from the original on 2015-08-28. Retrieved 2016-07-24.
- ^ Drake, R.L.; Vogl, W.; Mitchell, A.W.M. (2010). Gray's Anatomy for Students. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone.