
Back سلالة تانغ المتأخرة الحاكمة Arabic Sonrakı Tan AZ পরবর্তী তাং Bengali/Bangla Tang posteriors Catalan تانگی دواتر CKB Pozdní Tchang Czech Spätere Tang-Dynastie German Dinastía Tang posterior Spanish Myöhempi Tang-dynastia Finnish Tang postérieurs French
This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2008) |
Tang 唐 | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 923–937 | |||||||||||||||||||
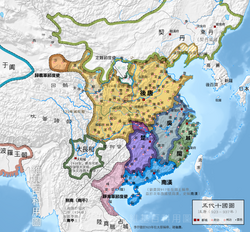 Later Tang 後唐 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Daming (923) Luoyang (923–936) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Chinese | ||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||||||||||
• 923–926 | Li Cunxu (Zhuangzong) | ||||||||||||||||||
• 926–933 | Li Siyuan (Mingzong) | ||||||||||||||||||
• 933–934 | Li Conghou | ||||||||||||||||||
• 934–936 | Li Congke | ||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period | ||||||||||||||||||
• Established in Daming | May 923 | ||||||||||||||||||
• Overthrown by Khitan and Shi Jingtang | January 11, 937 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Chinese coin, Chinese cash | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | China | ||||||||||||||||||
1.The preceding entity of the Later Tang was the State of Jin, which was established by Li Keyong in 895 under the Tang dynasty and existed as an independent state in 907–923. 2.With the support of the Liao dynasty. | |||||||||||||||||||
Tang, known in historiography as the Later Tang, was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China and the second of the Five Dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period in Chinese history.[1]
The first three of the Later Tang's four emperors were ethnically Shatuo.[2] The name Tang was used to legitimize itself as the restorer of the Tang dynasty. Although the Later Tang officially began in 923, the dynasty already existed in the years before, as a polity known in historiography as the Former Jin (907–923).
At its height, Later Tang controlled most of northern China.
- ^ Zurndorfer, Harriet T. (2010). "Efflorence? Another Look at the Role of War in Song Dynasty China". War in words transformations of war from antiquity to Clausewitz. Berlin: De Gruyter. p. 92. ISBN 9783110245424.
- ^ Mote 1999, pp. 12–13.