
Back بروتوكول ناغويا Arabic নাগোয়া প্ৰট'কল AS Nagoya Protocol BCL Nagojský protokol Czech Protocol Nagoya CY Nagoya-protokollen Danish Nagoya-Protokoll German Protocolo de Nagoya Spanish Nagoya protokoll ET پروتکل ناگویا FA
| Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization to the Convention on Biological Diversity | |
|---|---|
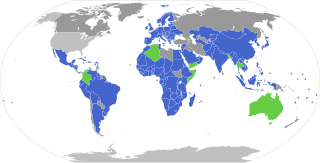 Parties
signed, but not ratified
non signatory, but Biological Diversity Convention party
non signatory, non-Biological Diversity Convention party
Besides several member states, the EU is also a party (not on map) | |
| Type | Environmental |
| Signed | 29 October 2010 |
| Location | Nagoya, Japan |
| Effective | 12 October 2014 |
| Condition | 50 ratifications |
| Signatories | 92 |
| Parties | 137 |
| Depositary | Secretary-General of the United Nations |
| Languages | Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian and Spanish |
The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization to the Convention on Biological Diversity, also known as the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS), is a 2010 supplementary agreement to the 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). Its aim is the implementation of one of the three objectives of the CBD: the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising out of the utilization of genetic resources, thereby contributing to the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity. It sets out obligations for its contracting parties to take measures in relation to access to genetic resources, benefit-sharing and compliance.
The protocol was adopted on 29 October 2010 in Nagoya, Japan, and entered into force on 12 October 2014. As of April 2022[update], it has been ratified by 137 parties, which includes 136 UN member states and the European Union.
Concerns have been expressed that the added bureaucracy and legislation could be damaging to the monitoring and collection of biodiversity, to conservation, to the international response to infectious diseases, and to research.[1][2]