
Back عصب حجابي Arabic Nervi frènic Catalan Nervus phrenicus German Nervio frénico Spanish Diafragma nerbio EU عصب میانبندی FA Nerf phrénique French Nervo frenico Italian 横隔神経 Japanese 가로막신경 Korean
| Phrenic nerve | |
|---|---|
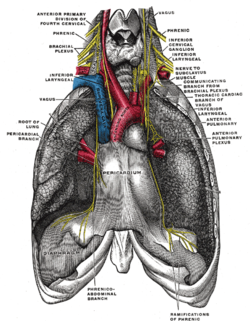 The phrenic nerve as it passes through the thorax to supply the diaphragm. | |
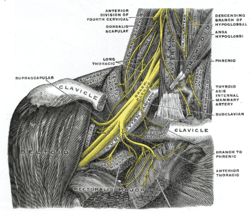 The phrenic nerve emerges from the cervical plexus, with the right brachial plexus shown here. | |
| Details | |
| From | C3–C5 of cervical plexus |
| Innervates | Diaphragm |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus phrenicus |
| MeSH | D010791 |
| TA98 | A14.2.02.028 |
| TA2 | 6380 |
| FMA | 6191 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The phrenic nerve is a mixed nerve that originates from the C3–C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In humans, the right and left phrenic nerves are primarily supplied by the C4 spinal nerve, but there is also a contribution from the C3 and C5 spinal nerves. From its origin in the neck, the nerve travels downward into the chest to pass between the heart and lungs towards the diaphragm.
In addition to motor fibers, the phrenic nerve contains sensory fibers, which receive input from the central tendon of the diaphragm and the mediastinal pleura, as well as some sympathetic nerve fibers. Although the nerve receives contributions from nerve roots of the cervical plexus and the brachial plexus, it is usually considered separate from either plexus.
The name of the nerve comes from Ancient Greek phren 'diaphragm'.[1]
- ^ O'Rahilly, Ronan (2008). Basic Human Anatomy. Hanover, New Hampshire: Geisel School of Medicine. Archived from the original on 20 March 2018. Retrieved 3 April 2019.