
Back حالة تسابق Arabic Yarış durumu AZ یاریشما دورومو AZB Situació de competició Catalan Souběh Czech Wettlaufsituation German Konkura kondiĉo EO Condición de carrera Spanish وضعیت رقابتی FA Situation de compétition French
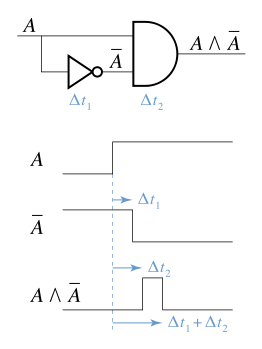
A race condition or race hazard is the condition of an electronics, software, or other system where the system's substantive behavior is dependent on the sequence or timing of other uncontrollable events, leading to unexpected or inconsistent results. It becomes a bug when one or more of the possible behaviors is undesirable.
The term race condition was already in use by 1954, for example in David A. Huffman's doctoral thesis "The synthesis of sequential switching circuits".[1]
Race conditions can occur especially in logic circuits or multithreaded or distributed software programs. Using mutual exclusion can prevent race conditions in distributed software systems.
- ^ Huffman, David A. "The synthesis of sequential switching circuits." (1954).