Back مترو سانتياغو Arabic Мэтрапалітэн Сант’яга BE-X-OLD Метрополитен на Сантяго Bulgarian সান্তিয়াগো মেট্রো Bengali/Bangla Metro de Santiago de Xile Catalan Metro v Santiagu Czech Metro de Santiago German Metroo de Santiago de Ĉilio EO Metro de Santiago Spanish Santiagoko metroa EU
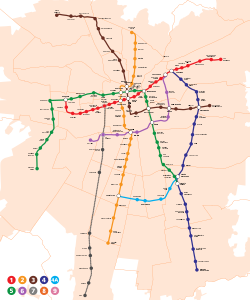
The Santiago Metro (Spanish: Metro de Santiago) is a rapid transit system serving the city of Santiago, the capital of Chile. It currently consists of seven lines (numbered 1-6 and 4A), 143 stations, and 149 kilometres (92.6 mi) of revenue route.[5] The system is managed by the state-owned Metro S.A. and is the first rapid transit system in the country.
The Santiago Metro carries around 2.5 million passengers daily. This figure represents an increase of more than a million passengers per day compared to 2007, when the ambitious Transantiago project was launched, in which the metro plays an important role in the public transport system serving the city. Its highest passenger peak was reached on 2 May 2019, reaching 2,951,962 passengers.[6]
In June 2017 the government announced plans for the construction of Line 7, connecting Renca in the northwest of Santiago with Vitacura in the northeast. The new line will add 26 kilometres (16 mi) and 19 new stations to the Metro network, running along the municipalities of Renca, Cerro Navia, Quinta Normal, Santiago, Providencia, Las Condes and Vitacura. Its cost has been initially estimated at US$2.53 bn, and it is projected to open in 2027.[7][8]
In March 2012, the Santiago Metro was chosen as the best underground system in the Americas, after being honoured at the annual reception held by Metro Rail in London.[9]
- ^ a b "Conoce la "estación fantasma" de la Línea 3: fue construida hace 30 años y no será utilizada" [Meet Line 3's "Ghost Station": Built 30 years ago and not used] (in Spanish). Bio Bio. 21 January 2019. Retrieved 2019-01-22.
- ^ a b "Memoria Integrada 2023" [Integrated Report 2023] (PDF) (in Spanish). Metro de Santiago. p. 10. Retrieved 2024-10-19.
- ^ "Corporativa – Historia – Historia de Metro" [Corporate – History – History of Metro] (in Spanish). Metro de Santiago. July 1, 2013. Retrieved 2013-09-18.
- ^ "La Tercera" (in Spanish). La Tercera. 25 September 2023.
- ^ Barra, Andrés (2023-09-25). "Extensión Línea 3: cómo queda el mapa del Metro de Santiago con las nuevas estaciones". La Tercera. Retrieved 2023-09-25.
- ^ "T13 | Tele 13". www.t13.cl. Retrieved 2021-02-25.
- ^ "Así será la nueva Línea 7 del Metro de Santiago". La Tercera (in Spanish). 2 June 2017. Retrieved 27 July 2017.
- ^ "Futura Línea 7 – Línea 3 y 6". www.metro.cl. Archived from the original on 2019-02-09. Retrieved 2021-07-29.
- ^ "Metro de Santiago es elegido como el mejor tren subterráneo de América". La Tercera (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 28 March 2012. Retrieved 29 November 2015.