
Back Streptomisien AF ستربتوميسين Arabic استرپتومایسین AZB Стрептомицин Bulgarian স্ট্রেপ্টোমাইসিন Bengali/Bangla Streptomicin BS Estreptomicina Catalan سترێپتۆمایسین CKB Streptomycin Czech Streptomycin CY
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | S/STR/STS[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 84% to 88% IM (est.)[2] 0% by mouth |
| Elimination half-life | 5 to 6 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.323 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
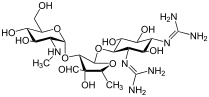
| Formula | C21H39N7O12 |
| Molar mass | 581.580 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 12 °C (54 °F) [citation needed] |
| |
| |
| | |
Streptomycin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections,[3] including tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium complex, endocarditis, brucellosis, Burkholderia infection, plague, tularemia, and rat bite fever.[3] For active tuberculosis it is often given together with isoniazid, rifampicin, and pyrazinamide.[4] It is administered by injection into a vein or muscle.[3]
Common side effects include vertigo, vomiting, numbness of the face, fever, and rash.[3] Use during pregnancy may result in permanent deafness in the developing baby.[3] Use appears to be safe while breastfeeding.[4] It is not recommended in people with myasthenia gravis or other neuromuscular disorders.[4] Streptomycin is an aminoglycoside.[3] It works by blocking the ability of 30S ribosomal subunits to make proteins, which results in bacterial death.[3]
Albert Schatz first isolated streptomycin in 1943 from Streptomyces griseus.[5][6] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[7] The World Health Organization classifies it as critically important for human medicine.[8]
- ^ "Antibiotic abbreviations list". Retrieved June 22, 2023.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Zhu2001was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g "Streptomycin Sulfate". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on December 20, 2016. Retrieved December 8, 2016.
- ^ a b c World Health Organization (2009). Stuart MC, Kouimtzi M, Hill SR (eds.). WHO Model Formulary 2008. World Health Organization. pp. 136, 144, 609. hdl:10665/44053. ISBN 9789241547659.
- ^ Torok E, Moran E, Cooke F (2009). Oxford Handbook of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology. OUP Oxford. p. Chapter 2. ISBN 9780191039621. Archived from the original on September 8, 2017.
- ^ Renneberg R, Demain AL (2008). Biotechnology for Beginners. Elsevier. p. 103. ISBN 9780123735812. Archived from the original on September 10, 2017.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). Critically important antimicrobials for human medicine (6th revision ed.). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/312266. ISBN 9789241515528. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.