
Back Tinzaparin German تینزاپارین سدیم FA Tinzaparină sodică Romanian Tinzaparin Swedish Тинзапарин Ukrainian
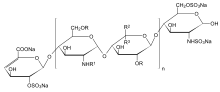 n = 1 to 25, R = H or SO3Na, R1 = H, SO3Na or COCH3, R2 = H and R3 = COONa or R2 = COONa and R3 = H | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | innohep(R) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Routes of administration | subcutaneous (once daily) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90% for Anti-Xa activity, 67% for Anti-IIa activity)[2] |
| Metabolism | minor metabolisation in liver by desulfation and/or depolymerization; excretion via kidneys in almost unchanged form |
| Elimination half-life | 200 min. for Anti-Xa activity, 257. min for Anti-IIa activity [3] |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.110.590 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Molar mass | 6500 g/mol (average)[4] |
| | |
Tinzaparin is an antithrombotic drug in the heparin group. It is a low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) marketed as Innohep worldwide. It has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for once daily treatment and prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE).[5]
It can be given subcutaneously by syringe, or intravenously.[6] It was manufactured by Leo pharmaceutical company, who withdrew the product from the US in 2011 due to low sales and a contamination issue.[7]
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ Cheer S.M. et al. Drugs 2004; 64 (13): 1479–1502
- ^ Pedersen P.C. et al. Thromb Res 1991; 61 (5-6): 477-487
- ^ European Pharmacopoeia, 6th Edition, 2008
- ^ Hull et al. NEJM 1992;326,15:975-982
- ^ Farmaceutiska Specialiteter i Sverige - the Swedish official drug catalog. Fass.se Archived 21 January 2011 at the Wayback Machine > Innohep
- ^ "Drug Shortages List". Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 4 October 2016.