Back فيروس ألفا Arabic فيروس الفا ARZ Alphavirus Czech Alphavirus German Alphavirus English Alphavirus Spanish Alfaviirus ET Alphavirus French अल्फावाइरस HI Альфавирустар KK
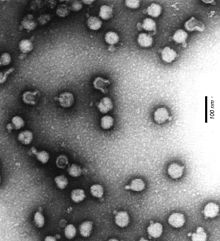
Alphavirus (nella letteratura in lingua italiana talora Alfavirus) è un genere di virus ad RNA a singolo filamento positivo, unico membro della famiglia dei Togaviridae, di medie dimensioni, forma rotondeggiante, nucleocapside a simmetria icosaedrica avvolto da membrana lipoproteica, in grado di infettare numerosi vertebrati per mezzo di artropodi[1]. Ubiquitari e distribuiti in sette gruppi sierologici[2], gli Alphavirus determinano due gruppi di patologie: encefaliti[3] e sindromi febbrili con eruzioni cutanee e poliartriti[4].
- ^ Weaver S C, Dalgarno L, Frey T K, et al. (editors), «Virus taxonomy. Classification and nomenclature of viruses». In: Seventh report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. San Diego, Calif: Academic Press, Inc., 2000. pp. 879–889
- ^ Powers AM, Brault AC, Shirako Y, et al. «Evolutionary relationships and systematics of the alphaviruses». J Virol. 2001 Nov;75(21):10118-31. PMID 11581380 ( Free article.
- ^ Steele KE, Twenhafel NA. «Review paper: pathology of animal models of alphavirus encephalitis». Vet Pathol. 2010 Sep;47(5):790-805. PMID 20551475
- ^ Harley D, Sleigh A, Ritchie S. «Ross River virus transmission, infection, and disease: a cross-disciplinary review». Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001 Oct;14(4):909-32, PMID 11585790 ( Free article.