
Back Jordaanrivier AF Iordan ANG Okwaan̄ Jodan ANN نهر الأردن Arabic ܢܗܪܐ ܕܝܘܪܕܢܢ ARC نهر الاردن ARZ İordan çayı AZ اوردن چایی AZB Иордан BA Jordan BAR
| Jordan River | |
|---|---|
 Jordan River | |
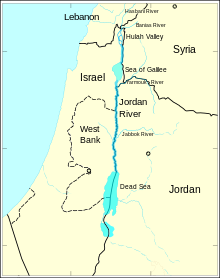 The Jordan River runs along the border between Jordan, the Palestinian West Bank, Israel and southwestern Syria. | |
| Etymology | Hebrew: ירדן (yardén, "descender"), from ירד (yarad, "descended")[1] |
| Location | |
| Country | Jordan, Israel, Syria, Palestine |
| Region | Middle East, Eastern Mediterranean littoral |
| District | Galilee |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| - location | Anti-Lebanon Mountain Range at Mount Hermon, Golan Heights |
| - elevation | 2,814 m (9,232 ft) |
| Mouth | Dead Sea |
| - elevation | −416 m (−1,365 ft) |
| Length | 251 km (156 mi) |
| Discharge | |
| - location | Dead Sea, Jordan Rift Valley |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| - left | Banias River, Dan River, Yarmouk River, Zarqa River |
| - right | Hasbani or Snir River, Iyyon Stream |
The Jordan River (Hebrew: נהר הירדן nehar hayarden, Arabic: نهر الأردن nahr al-urdun) is a river in Southwest Asia that flows through the Great Rift Valley into the Dead Sea. Many people think it is one of the world's most sacred rivers.
It is 251 kilometres (156 mi) long. Its tributaries are:
- The Hasbani (Hebrew: שנירsenir, Arabic: الحاصباني hasbani), which flows from Lebanon.
- The Banias (Hebrew: חרמון hermon, Arabic: بانياس banias), that comes from a spring at Banias at the foot of Mount Hermon.
- The Dan (Hebrew: דן dan, Arabic: اللدان leddan) with its source at the foot of Mount Hermon.
- The Ayoun (Hebrew: עיון ayoun, Arabic: عيون ayoun), which flows from Lebanon.
The four rivers join to form the Jordan in northern Israel, near kibbutz Sede Nehemya. The Jordan drops quickly in a 75 kilometer run to Lake Hula, which is a little below sea level in the Galilee sea. Then it drops much more in about 25 kilometers to the Sea of Galilee. The last section has less gradient, and the river begins to twist before it enters the Dead Sea, which is about 400 meters below sea level and has no outlet. Two major tributaries enter this last section from the east: the Yarmouk River and Jabbok River.
In 1964, Israel began operating a dam that takes water from the Sea of Galilee, a major Jordan River water provider, to the national water carrier. Also in 1964 Jordan built a channel that takes water from the Yarmouk River, a main tributary of the Jordan River. This caused great damage to the ecosystem. Syria has also built reservoirs that catch the Yarmouk's waters.
In modern times, 70% to 90% of the waters is used for human purposes and the flow is much smaller. Because of this, and the high evaporation rate of the Dead Sea, the sea is shrinking. All the shallow waters of the southern end of the sea have been drained in modern times, and are now salt flats.
The water from the Jordan is a very important resource to the dry lands of the area. It is a source of conflict between Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Israel and Palestine.
- ↑ Klein, Ernest, A Comprehensive Etymological Dictionary of the Hebrew Language for Readers of English, The University of Haifa, Carta, Jerusalem, p. 264