
Back Kapampangan AF ካፓምፓንጋንኛ AM لغة كابامبانجان Arabic Idioma pampangu AST کاپامپانقان دیلی AZB Tataramon na Pampango BCL Капампанганская мова BE Kapampanganeg BR Pampanga (llengua) Catalan Kapampangan-ngṳ̄ CDO
| Kapampangan | |
|---|---|
| Pampangan | |
| Amánung Kapampangan, Amánung Sísuan | |
 "Kapampangan" written in Kulitan, the native writing system of the language | |
| Pronunciation | [kapamˈpaŋan] |
| Native to | Philippines (Central Luzon) |
| Region | Pampanga, southern Tarlac, northeastern Bataan, western Bulacan, southwestern Nueva Ecija and southeastern parts of Zambales |
| Ethnicity | Kapampangan people |
Native speakers | 2.4 million (2010)[1] |
| Dialects | |
| Latin (Kapampangan alphabet) Historically written in: Kulitan | |
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in | Regional language of the Philippines |
| Regulated by | Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | pam |
| ISO 639-3 | pam |
| Glottolog | pamp1243 |
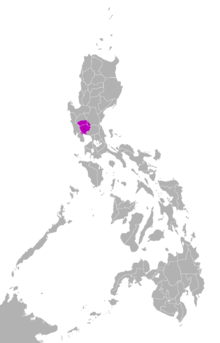 | |
The Pampangan language or Kapampangan is one of the main languages of the Philippines. It is predominantly spoken in the province of Pampanga, and most parts of Tarlac towns in Bamban, Capas, Concepcion, La Paz and Tarlac City and Bataan.
- ↑ Kapampangan at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)