
Back Entstof AF Vacuna AN टीका ANP لقاح Arabic طوعم ARZ ছিটা AS Vacuna AST Peyvənd AZ Вакцина BA Čieps BAT-SMG
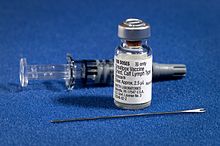
A vaccine is a biological preparation. It is given to prevent a specific infectious or malignant disease. It only works against the microorganism for which it is prepared. It is usually given by injection, and called vaccination.

At its best, vaccination gives immunity to an infectious disease caused by a particular microorganism (bacteria or virus). For example, the flu vaccine makes it very much less likely that a person will get the flu. The flu virus continually changes, and has many strains. That is why re-vaccination is needed every year.
At first, vaccines were usually made from something that is alive, or was alive. Now they may be built up by viral biochemistry. Each vaccine has its own history, and what is true of one might not be true of another.
The word "vaccine" comes from the Latin vacca, meaning "cow"). In 1796, Edward Jenner used a milkmaid infected with cowpox (variolae vaccinae) to protect people against smallpox.[1] The use of vaccines is called vaccination.
Vaccination had been done before Jenner.[2] Powdered smallpox material was blown up the nostrils of the subject.
- ↑ Stern A.M. & Markel H. (2005). "The history of vaccines and immunization: familiar patterns, new challenges". Health Affairs. 24 (3): 611–21. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.24.3.611. PMID 15886151.
- ↑ Williams G 2010. Angel of Death. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-230-27471-6