
Back تصيير (رسوميات حاسوبية) Arabic Render AZ Рендъринг Bulgarian চিত্রায়ন (পরিগণক চিত্রলিখন) Bengali/Bangla Render (računarska grafika) BS Renderització Catalan Renderování Czech Rendere Danish Bildsynthese German Απόδοση (γραφικά υπολογιστή) Greek
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2020) |
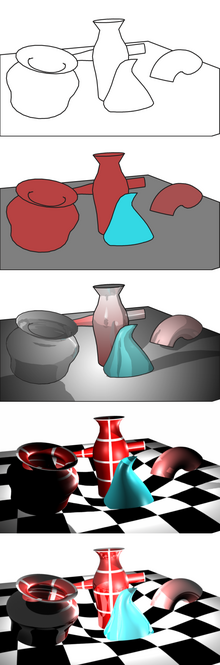

Rendering or image synthesis is the process of generating a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image from a 2D or 3D model by means of a computer program.[citation needed] The resulting image is referred to as the render. Multiple models can be defined in a scene file containing objects in a strictly defined language or data structure. The scene file contains geometry, viewpoint, textures, lighting, and shading information describing the virtual scene. The data contained in the scene file is then passed to a rendering program to be processed and output to a digital image or raster graphics image file. The term "rendering" is analogous to the concept of an artist's impression of a scene. The term "rendering" is also used to describe the process of calculating effects in a video editing program to produce the final video output.
A software application or component that performs rendering is called a rendering engine,[1] render engine, rendering system, graphics engine, or simply a renderer.
Rendering is one of the major sub-topics of 3D computer graphics, and in practice it is always connected to the others. It is the last major step in the graphics pipeline, giving models and animation their final appearance. With the increasing sophistication of computer graphics since the 1970s, it has become a more distinct subject.
Rendering has uses in architecture, video games, simulators, movie and TV visual effects, and design visualization, each employing a different balance of features and techniques. A wide variety of renderers are available for use. Some are integrated into larger modeling and animation packages, some are stand-alone, and some are free open-source projects. On the inside, a renderer is a carefully engineered program based on multiple disciplines, including light physics, visual perception, mathematics, and software development.
Though the technical details of rendering methods vary, the general challenges to overcome in producing a 2D image on a screen from a 3D representation stored in a scene file are handled by the graphics pipeline in a rendering device such as a GPU. A GPU is a purpose-built device that assists a CPU in performing complex rendering calculations. If a scene is to look relatively realistic and predictable under virtual lighting, the rendering software must solve the rendering equation. The rendering equation does not account for all lighting phenomena, but instead acts as a general lighting model for computer-generated imagery.
In the case of 3D graphics, scenes can be pre-rendered or generated in realtime. Pre-rendering is a slow, computationally intensive process that is typically used for movie creation, where scenes can be generated ahead of time, while real-time rendering is often done for 3D video games and other applications that must dynamically create scenes. 3D hardware accelerators can improve realtime rendering performance.